Understanding and Calibrating the GM 2-Bar MAP Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding and Calibrating the GM 2-Bar MAP Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Calibrating the GM 2-Bar MAP Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Calibrating the GM 2-Bar MAP Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide
![[DIAGRAM] Gm 2 Bar Map Sensor Wiring Diagram - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://www.efihardware.com/images/2923/H-MAPDelco1BarMAPSensorWiringRevision1.jpg?cache=20150412230602)
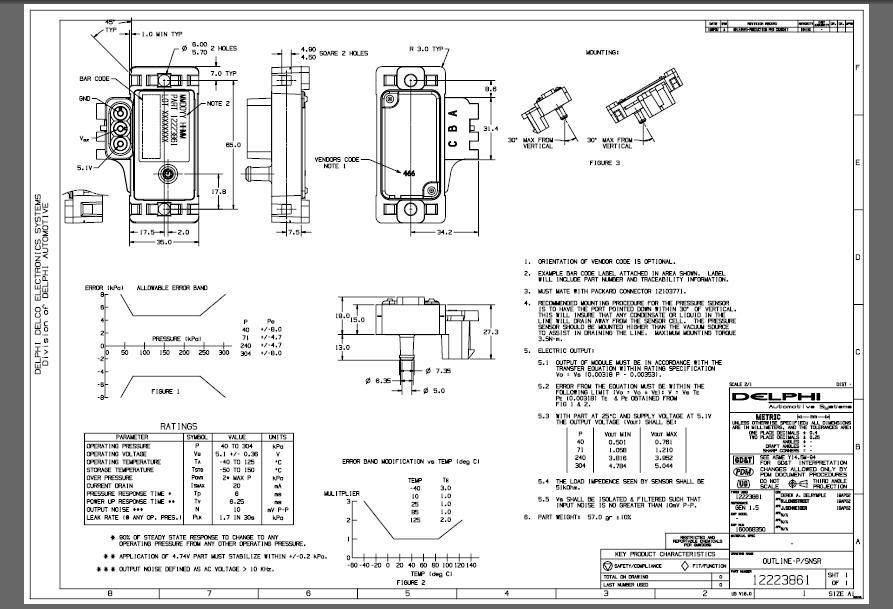
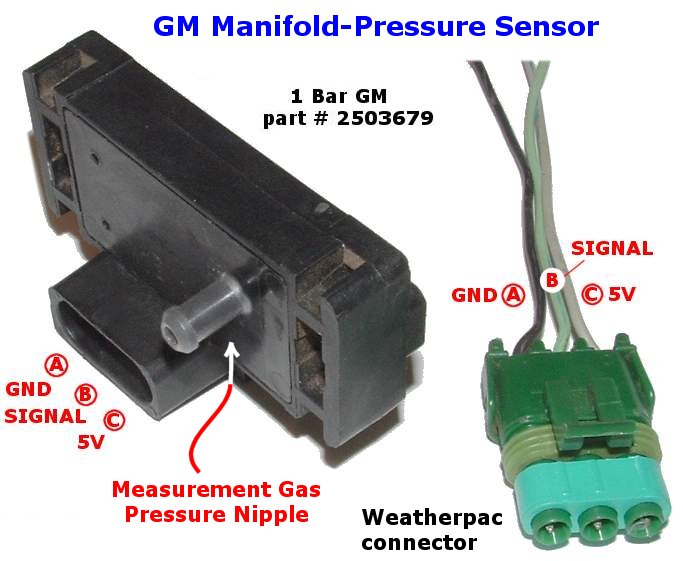
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor is a critical component in modern automotive engine management systems. It plays a vital role in determining engine load and adjusting fuel delivery and ignition timing for optimal performance and fuel efficiency. Within the spectrum of MAP sensors, the 2-bar sensor, commonly found in GM vehicles, stands out due to its ability to measure higher manifold pressures, enabling the use of forced induction systems such as turbochargers and superchargers.
This article delves into the intricacies of the GM 2-bar MAP sensor, exploring its operation, calibration process, and the significance of accurate calibration for engine performance.
The Function of the MAP Sensor:
The MAP sensor is a crucial component in the engine control unit (ECU)’s ability to understand the conditions within the engine’s intake manifold. It measures the absolute pressure within the manifold, which is a direct indicator of engine load. Higher manifold pressure signifies a heavier load on the engine, necessitating adjustments to fuel delivery and ignition timing to maintain efficient combustion.
The Role of the 2-Bar MAP Sensor:
Standard MAP sensors typically operate within a pressure range of 0 to 1 bar (14.5 psi). However, vehicles equipped with forced induction systems require a sensor capable of measuring higher pressures. This is where the 2-bar MAP sensor comes into play. It can measure pressures up to 2 bars (29 psi), accommodating the increased pressure generated by turbochargers or superchargers.
The Calibration Process:
Calibration of the MAP sensor involves ensuring that the sensor’s output voltage accurately corresponds to the actual manifold pressure. This is crucial for the ECU to interpret the sensor data correctly and make appropriate adjustments to engine parameters.
Why Calibration is Essential:
- Accurate Load Sensing: A properly calibrated MAP sensor ensures that the ECU receives accurate information about engine load, enabling it to optimize fuel delivery and ignition timing.
- Enhanced Performance: Accurate load sensing translates into smoother engine operation, better throttle response, and improved power delivery.
- Reduced Fuel Consumption: Precise fuel delivery based on accurate load data minimizes fuel waste, contributing to better fuel economy.
- Emissions Control: Proper calibration helps ensure optimal combustion, reducing harmful emissions and contributing to cleaner air.
Calibration Methods:
Calibration of the GM 2-bar MAP sensor typically involves two primary methods:
1. Software-Based Calibration:
- Using a Scan Tool: Most modern vehicles allow for sensor calibration through a scan tool. The scan tool connects to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and provides access to the ECU’s settings.
- Calibration Procedure: The calibration procedure usually involves entering a specific sequence of commands or selecting a calibration option within the scan tool’s menu.
- Calibration Data: The scan tool may require the user to input specific calibration data, such as the sensor’s reference voltage or pressure range.
2. Hardware-Based Calibration:
- Using a Calibration Tool: Specialized calibration tools are available for specific MAP sensor types, including the GM 2-bar sensor. These tools typically connect to the sensor’s wiring harness and provide a controlled pressure source.
- Calibration Process: The tool applies a known pressure to the sensor and measures the resulting output voltage. The tool then adjusts the sensor’s internal calibration parameters to match the expected voltage output.
Signs of a Faulty MAP Sensor:
- Engine Stalling or Rough Idle: A faulty MAP sensor can lead to inaccurate load sensing, causing the engine to stall or run rough.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Incorrect load information can result in excessive fuel consumption.
- Lack of Power: A malfunctioning MAP sensor can hinder engine performance, resulting in sluggish acceleration and reduced power output.
- Check Engine Light: The ECU may detect a fault with the MAP sensor and illuminate the check engine light.
Tips for Maintaining the MAP Sensor:
- Regular Inspections: Visually inspect the MAP sensor for signs of damage, dirt, or debris.
- Cleaning: Clean the sensor with a non-abrasive cleaner and compressed air if necessary.
- Replace if Necessary: If the sensor is damaged or shows signs of wear, replace it with a genuine GM part.
FAQs about GM 2-Bar MAP Sensor Calibration:
Q: Can I calibrate the MAP sensor myself?
A: While some basic calibrations can be performed using a scan tool, it is generally recommended to seek professional assistance for accurate and safe calibration.
Q: How often should I calibrate the MAP sensor?
A: Regular calibration is not typically required unless the sensor is suspected to be faulty or the vehicle has undergone significant modifications.
Q: What are the potential consequences of an uncalibrated MAP sensor?
A: An uncalibrated MAP sensor can lead to engine performance issues, reduced fuel efficiency, increased emissions, and even damage to the engine if left unchecked.
Q: Can I use a generic MAP sensor instead of a GM 2-bar sensor?
A: Using a generic sensor may not be compatible with the vehicle’s ECU and could lead to inaccurate readings and engine problems. It is recommended to use a genuine GM 2-bar sensor for optimal compatibility.
Conclusion:
The GM 2-bar MAP sensor plays a crucial role in optimizing engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. Accurate calibration of this sensor is essential for ensuring that the ECU receives reliable information about engine load. While software-based calibration using a scan tool is often feasible, hardware-based calibration with specialized tools may be necessary for more precise adjustments.
By understanding the importance of MAP sensor calibration and following the recommended maintenance practices, vehicle owners can ensure optimal engine performance and contribute to a cleaner environment.
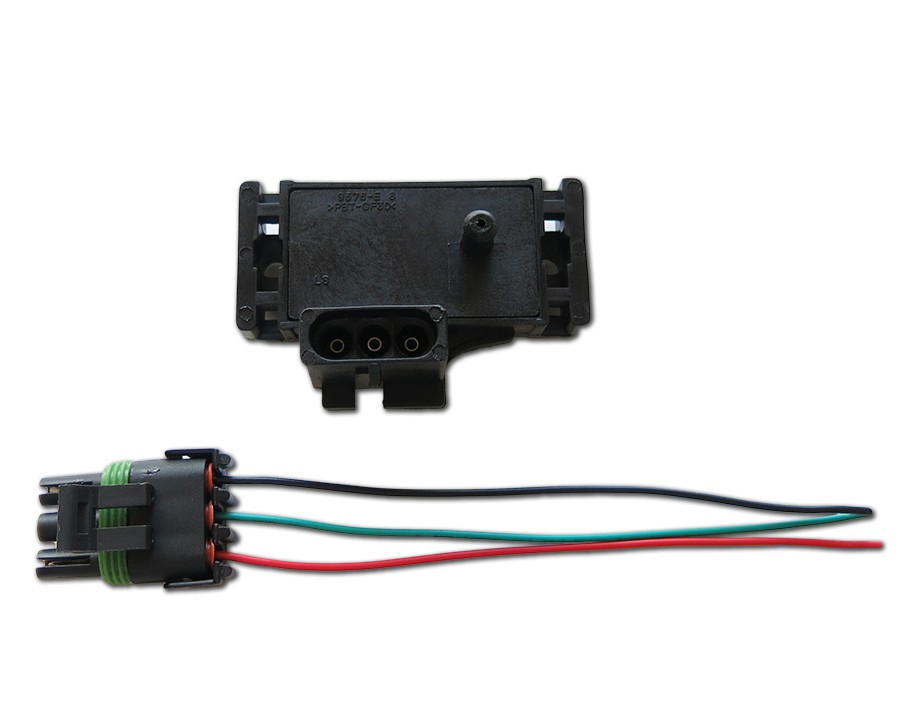



![[DIAGRAM] Gm 2 Bar Map Sensor Wiring Diagram - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://www.efihardware.com/images/4805/H-MAPLS1-2.jpg?cache=20141202095240)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Calibrating the GM 2-Bar MAP Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
