Understanding the 2004 Mazda 6 MAP Sensor: Location, Function, and Importance
Related Articles: Understanding the 2004 Mazda 6 MAP Sensor: Location, Function, and Importance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the 2004 Mazda 6 MAP Sensor: Location, Function, and Importance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the 2004 Mazda 6 MAP Sensor: Location, Function, and Importance

The 2004 Mazda 6, like many modern vehicles, relies on a sophisticated network of sensors to ensure optimal engine performance. One such crucial component is the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor. This small, yet vital sensor plays a critical role in engine management, directly influencing fuel delivery and ignition timing for efficient combustion.
Location and Identification
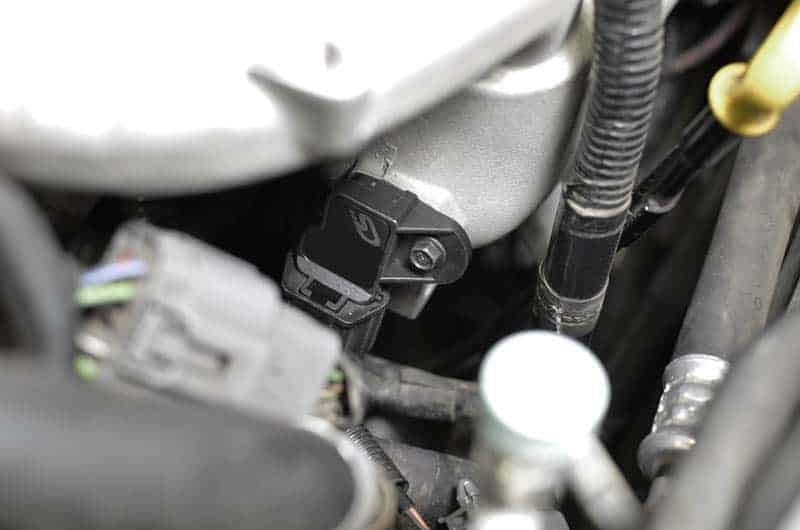
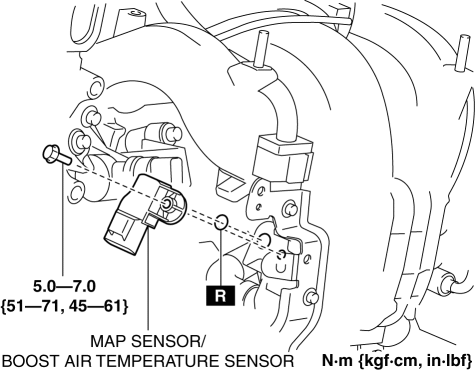
The MAP sensor in a 2004 Mazda 6 is typically located on the intake manifold, positioned near the throttle body. It’s a compact, cylindrical device with a single electrical connector. Visually, it may resemble a small, black or grey cylinder with a wire harness attached.
Function: The Heart of Engine Management
The MAP sensor’s primary function is to measure the absolute pressure within the intake manifold. This pressure, known as manifold absolute pressure (MAP), provides a direct indication of the amount of air entering the engine during each intake stroke.
Here’s how it works:
- Air Intake: As the engine draws in air through the intake manifold, the MAP sensor senses the pressure within the manifold.
- Signal Transmission: This pressure reading is converted into an electrical signal by the sensor.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): The ECU receives this signal and uses it to determine the appropriate amount of fuel to inject and the timing for ignition.
Importance: Ensuring Efficient Combustion
The MAP sensor plays a crucial role in achieving optimal engine performance. Its accurate readings ensure:
- Precise Fuel Delivery: By providing the ECU with real-time information about the air intake, the MAP sensor allows for accurate fuel injection. This ensures the correct fuel-to-air ratio for efficient combustion, maximizing power output and minimizing emissions.
- Optimized Ignition Timing: The ECU utilizes the MAP sensor readings to determine the optimal timing for spark delivery. This ensures that the fuel-air mixture ignites at the ideal moment, maximizing combustion efficiency and reducing engine knock.
- Smooth Engine Operation: The MAP sensor’s contribution to precise fuel and ignition control directly translates to smoother engine operation, enhancing driving comfort and minimizing vibrations.
Signs of a Faulty MAP Sensor
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to various engine problems, including:
- Rough Idling: The engine may idle erratically, stalling or surging.
- Poor Acceleration: The car may struggle to accelerate, feeling sluggish or unresponsive.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: Inaccurate fuel delivery due to a faulty MAP sensor can lead to increased fuel consumption.
- Check Engine Light: A malfunctioning MAP sensor will typically trigger the check engine light on the dashboard.
FAQs
Q: What are the common causes of a faulty MAP sensor?
A: Common causes include:
- Physical Damage: The sensor can be damaged due to exposure to extreme temperatures, vibrations, or even debris.
- Electrical Issues: A broken wire or loose connection in the sensor’s wiring harness can disrupt its functionality.
- Contamination: Dust, dirt, or oil buildup on the sensor’s diaphragm can affect its accuracy.
Q: How can I test the MAP sensor?
A: You can use a multimeter to test the sensor’s electrical output or utilize a scan tool to read its readings. However, it’s recommended to consult a qualified mechanic for proper testing and diagnosis.
Q: Can I replace the MAP sensor myself?
A: While replacing a MAP sensor is a relatively straightforward task, it’s recommended to seek professional assistance, especially if you lack experience with automotive repairs.
Tips
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspecting the MAP sensor for signs of damage, contamination, or loose connections can help prevent issues.
- Professional Diagnosis: If you suspect a faulty MAP sensor, it’s essential to have it professionally diagnosed to avoid misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs.
- Quality Parts: When replacing a MAP sensor, always use genuine or high-quality aftermarket parts to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor is an indispensable component in the 2004 Mazda 6’s engine management system. Its accurate readings are crucial for achieving efficient combustion, optimal fuel delivery, and smooth engine operation. Understanding the function and importance of the MAP sensor can help you identify potential issues and ensure your Mazda 6 continues to perform at its best. Remember, regular maintenance, professional diagnosis, and quality replacement parts are key to maintaining a healthy and reliable engine.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the 2004 Mazda 6 MAP Sensor: Location, Function, and Importance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
