Understanding the Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP Sensor) in Modern Engines
Related Articles: Understanding the Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP Sensor) in Modern Engines
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP Sensor) in Modern Engines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP Sensor) in Modern Engines

The modern internal combustion engine is a marvel of engineering, a complex system that relies on a delicate interplay of components to convert fuel into usable power. One crucial element in this intricate dance is the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP Sensor). This unassuming sensor plays a vital role in ensuring efficient and reliable engine operation, influencing critical parameters such as fuel delivery, ignition timing, and emissions control.
The MAP Sensor: A Window into Engine Intake Conditions
The MAP Sensor acts as a vital communication bridge between the engine’s intake manifold and the engine control unit (ECU). Its primary function is to measure the absolute pressure within the intake manifold, providing the ECU with real-time data on the amount of air entering the engine. This information is crucial for various engine management functions, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
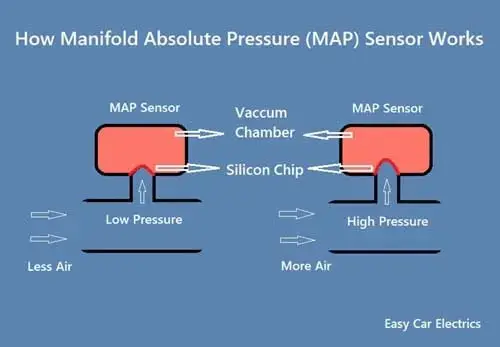
How the MAP Sensor Works: A Detailed Explanation
The MAP Sensor operates on the principle of piezoresistive technology. It contains a small diaphragm that is sensitive to pressure changes. When air enters the intake manifold, the pressure pushes on the diaphragm, causing it to deform. This deformation alters the electrical resistance within the sensor, generating a voltage signal proportional to the pressure.
This voltage signal is then transmitted to the ECU, which interprets it to determine the absolute pressure within the intake manifold. This pressure value, along with other sensor inputs, allows the ECU to calculate various critical parameters, including:
- Air-Fuel Ratio: The ECU uses the MAP sensor data to determine the amount of air entering the engine. This information is then used to calculate the precise amount of fuel required for optimal combustion, ensuring a balanced air-fuel mixture.
- Ignition Timing: The MAP sensor data allows the ECU to adjust the timing of the spark plugs, maximizing engine power and efficiency while minimizing emissions.
- Emissions Control: The MAP sensor plays a crucial role in emissions control systems by providing the ECU with information about the engine’s operating conditions. This data allows the ECU to adjust the operation of catalytic converters and other emissions control devices to minimize harmful pollutants.
The Importance of a Functional MAP Sensor: Ensuring Optimal Engine Performance
A properly functioning MAP sensor is essential for optimal engine performance and efficiency. A faulty or malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to a variety of problems, including:
- Poor Fuel Economy: An inaccurate reading from the MAP sensor can result in an imbalanced air-fuel mixture, leading to increased fuel consumption and reduced engine efficiency.
- Reduced Power Output: A malfunctioning MAP sensor can disrupt the engine’s timing and fuel delivery, leading to a noticeable decrease in power output and overall performance.
- Rough Idle and Stalling: An inaccurate MAP sensor reading can cause erratic engine operation, leading to rough idling, stalling, and difficulty starting the engine.
- Increased Emissions: A faulty MAP sensor can lead to an imbalanced air-fuel mixture, resulting in increased emissions of harmful pollutants.
Recognizing the Signs of a Failing MAP Sensor: Identifying Potential Issues
Identifying a failing MAP sensor can be challenging as the symptoms often mimic other engine problems. However, several telltale signs can indicate a potential issue:
- Check Engine Light (CEL): The most common indicator of a failing MAP sensor is the illumination of the check engine light. The ECU will usually store a diagnostic code related to a malfunctioning MAP sensor, allowing a mechanic to pinpoint the problem.
- Engine Stalling or Difficulty Starting: A malfunctioning MAP sensor can disrupt the engine’s idle and starting functions, leading to stalling or difficulty starting the engine, particularly in cold weather.
- Reduced Power and Acceleration: A failing MAP sensor can cause a noticeable decrease in engine power and acceleration, making it difficult to accelerate smoothly or maintain speed.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: An inaccurate MAP sensor reading can lead to an imbalanced air-fuel mixture, resulting in increased fuel consumption and reduced engine efficiency.
- Rough Idle and Engine Vibration: A faulty MAP sensor can cause erratic engine operation, leading to rough idling and noticeable engine vibration.
Troubleshooting and Repairing a Faulty MAP Sensor: A Step-by-Step Guide
If you suspect a malfunctioning MAP sensor, it’s essential to diagnose the problem accurately before attempting any repairs. This involves a combination of visual inspection, diagnostic testing, and component replacement:
- Visual Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the MAP sensor for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Diagnostic Testing: Use a scan tool to read the diagnostic codes stored in the ECU. These codes can provide valuable information about the specific issue with the MAP sensor.
- Pressure Testing: A pressure test can be performed to verify the sensor’s accuracy by applying a known pressure to the sensor and comparing the output signal to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Component Replacement: If the diagnostic testing confirms a faulty MAP sensor, it should be replaced with a new, compatible unit.
FAQs Regarding the MAP Sensor: Addressing Common Queries
Q: How often should the MAP sensor be replaced?
A: The MAP sensor is generally a long-lasting component with a lifespan of several years. However, factors like environmental conditions, engine wear, and driving habits can affect its longevity. It’s recommended to have the sensor inspected during routine maintenance checks or if you experience any of the symptoms associated with a failing sensor.
Q: Can I clean the MAP sensor to restore its functionality?
A: While cleaning a MAP sensor might seem like a viable solution, it is generally not recommended. The sensor’s delicate internal components can be easily damaged during cleaning, potentially leading to further problems. It’s best to replace a faulty sensor rather than attempting to clean it.
Q: What are the different types of MAP sensors available?
A: MAP sensors are available in various designs and configurations, depending on the specific vehicle and engine model. The most common types include:
- Piezoresistive MAP Sensors: These sensors use a diaphragm to measure pressure changes, converting them into electrical signals.
- Capacitive MAP Sensors: These sensors utilize a capacitor that changes capacitance based on pressure changes, generating an electrical signal.
Q: How can I prevent MAP sensor problems in the future?
A: While you cannot completely eliminate the risk of MAP sensor failure, following these tips can help prolong its lifespan:
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure regular maintenance checks, including inspection of the MAP sensor for signs of wear or damage.
- Clean Intake System: A clean intake system reduces the buildup of dirt and debris that can affect the sensor’s operation.
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Using high-quality fuel helps prevent the buildup of deposits within the intake manifold, which can impact the sensor’s performance.
Conclusion: The MAP Sensor’s Crucial Role in Modern Engine Management
The MAP sensor, though often overlooked, plays a vital role in modern engine management systems. It provides the ECU with real-time data about the engine’s intake conditions, enabling optimal fuel delivery, ignition timing, and emissions control. Recognizing the signs of a failing MAP sensor and addressing the issue promptly is crucial for maintaining engine performance, efficiency, and longevity. By understanding the function and importance of this vital component, drivers can ensure their vehicles operate at their peak performance and efficiency, contributing to a smoother, more enjoyable driving experience.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP Sensor) in Modern Engines. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
