Understanding the Impact of Southern California Earthquakes: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Impact of Southern California Earthquakes: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Impact of Southern California Earthquakes: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Impact of Southern California Earthquakes: A Comprehensive Guide

Southern California is a region renowned for its vibrant culture, stunning landscapes, and thriving economy. However, beneath its surface lies a dynamic geological reality, characterized by frequent seismic activity. The region sits atop the San Andreas Fault, a major fault line that marks the boundary between the Pacific and North American tectonic plates. This geological setting makes earthquakes a constant threat, demanding a comprehensive understanding of their causes, impacts, and preparedness strategies.
The Science Behind Southern California Earthquakes:
Earthquakes occur when the Earth’s tectonic plates, massive rock slabs that make up the planet’s outer layer, move against each other. The San Andreas Fault is a transform fault, where the plates slide horizontally past one another. This movement is not smooth, and the plates often become locked, accumulating stress over time. When this stress exceeds the strength of the rocks, the plates suddenly slip, releasing energy in the form of seismic waves that propagate through the Earth’s crust. These waves cause the ground to shake, resulting in an earthquake.
Magnitude and Intensity: Understanding Earthquake Measurements:
The magnitude of an earthquake is a measure of the energy released at its source, known as the epicenter. It is determined using the Richter scale, a logarithmic scale where each whole number increase represents a tenfold increase in the amplitude of seismic waves and approximately a 32-fold increase in energy released. For example, a magnitude 6 earthquake releases about 32 times more energy than a magnitude 5 earthquake.
Intensity, on the other hand, describes the effects of an earthquake at a particular location. It is measured using the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale, which assigns Roman numerals from I to XII based on the observed effects of ground shaking, damage to structures, and human perception. A higher intensity indicates a stronger shaking and greater damage.
The 5.8 Magnitude Earthquake: A Recent Example:
While the exact date and location of a 5.8 magnitude earthquake in Southern California are not specified in the prompt, it is important to understand the potential impacts of such a significant event. A magnitude 5.8 earthquake can cause substantial damage, particularly in areas with poorly constructed buildings or infrastructure. The shaking can lead to:
- Building collapse: Older or poorly designed buildings are more susceptible to collapse during strong earthquakes.
- Infrastructure damage: Roads, bridges, power lines, and pipelines can be severely damaged, disrupting transportation, communication, and essential services.
- Landslides and ground failures: Earthquakes can trigger landslides and soil liquefaction, particularly in areas with steep slopes or loose soil.
- Tsunami: While less likely in Southern California than in coastal regions of the Pacific Ocean, large earthquakes can generate tsunamis, which are giant waves capable of causing widespread devastation.
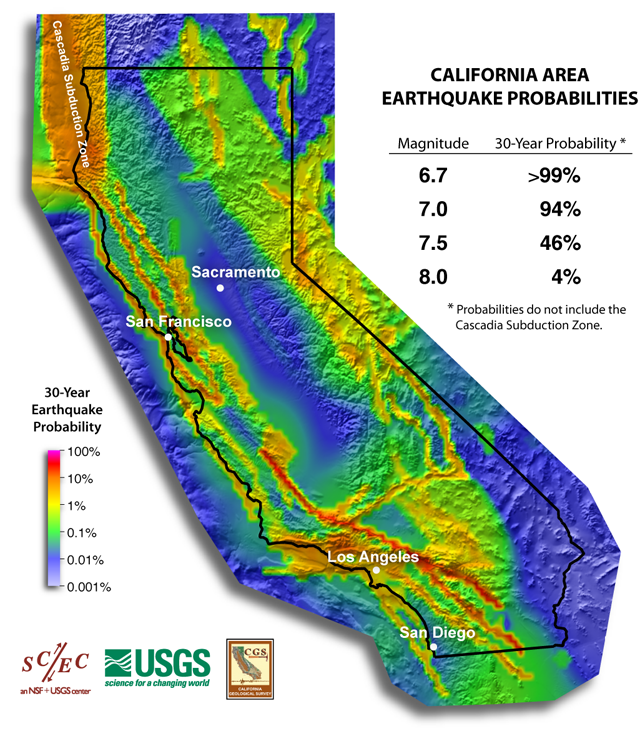
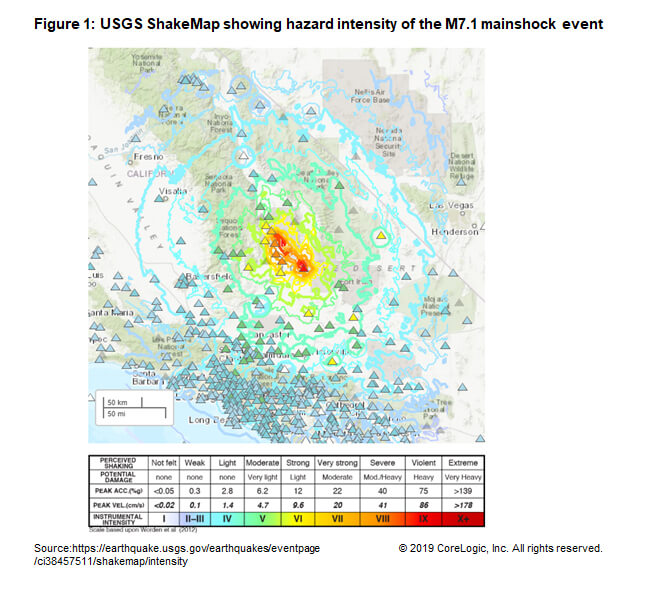
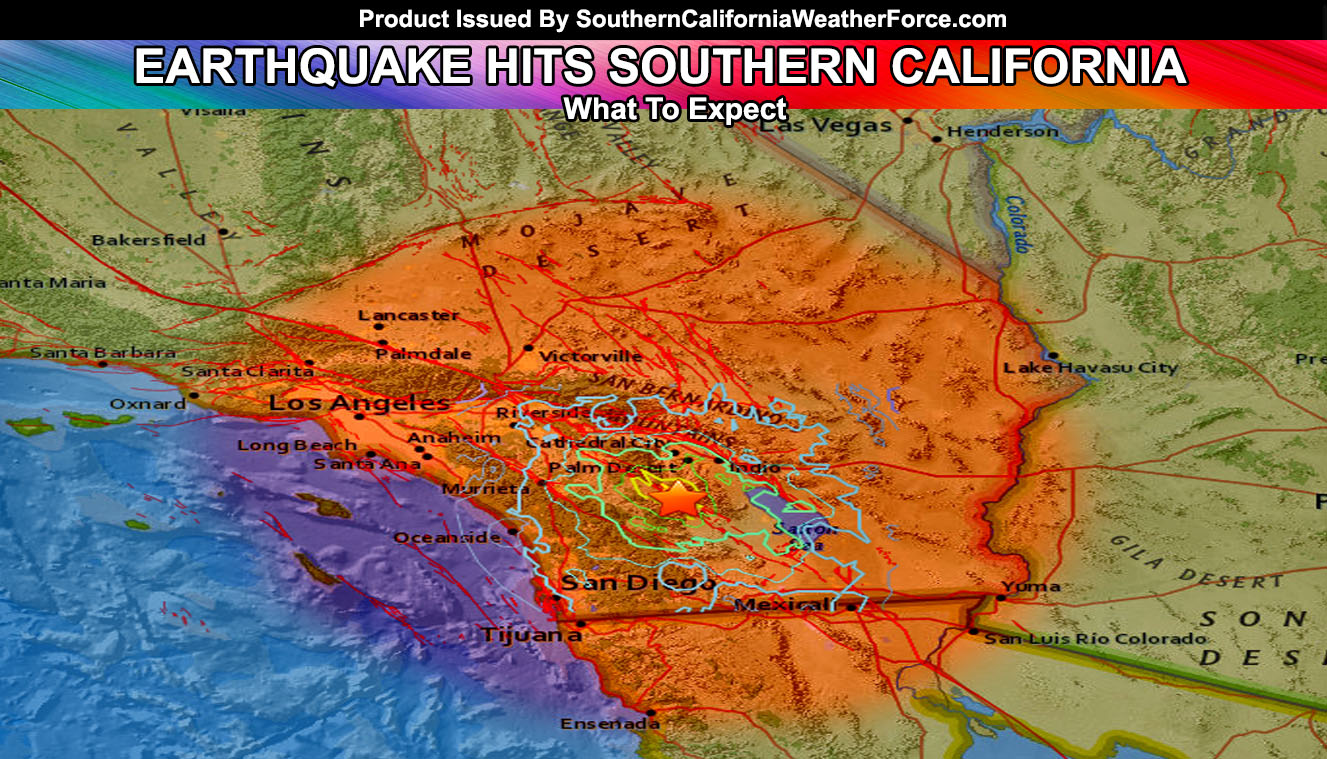
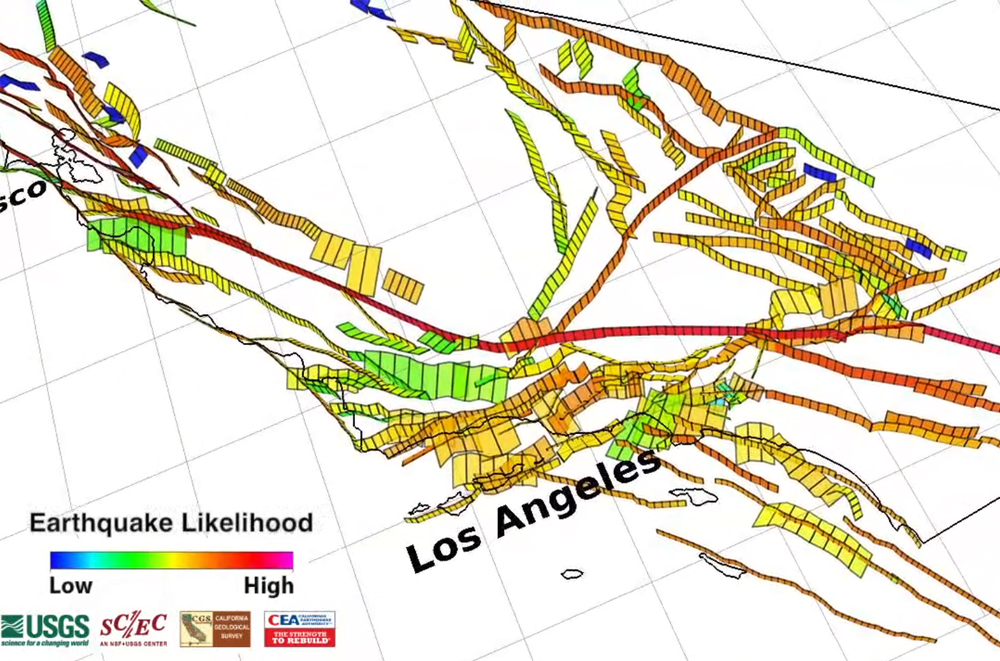
Mapping the Earthquake’s Impact:
Mapping the earthquake’s impact is crucial for understanding the extent of damage and directing emergency response efforts. Seismic networks, equipped with sensors that detect ground motion, provide real-time data used to pinpoint the epicenter, determine the magnitude, and assess the intensity of shaking across the affected region. This data is used to create maps that show the distribution of ground shaking, allowing for a more targeted response.
Preparedness and Mitigation Strategies:
Understanding the risks posed by earthquakes is essential for developing effective preparedness and mitigation strategies. These include:
- Building codes and seismic retrofitting: Enforcing strict building codes and retrofitting existing structures to meet seismic standards can significantly reduce the risk of damage and collapse.
- Emergency preparedness plans: Individuals, families, businesses, and communities should develop comprehensive emergency plans that include evacuation routes, communication protocols, and supplies for potential displacement.
- Public education and awareness: Raising public awareness about earthquake hazards, preparedness measures, and safety precautions is vital for minimizing the impacts of future events.
- Early warning systems: Advanced early warning systems can provide precious seconds or even minutes of warning before the arrival of strong shaking, allowing people to take cover or shut down critical infrastructure.
FAQs Regarding Southern California Earthquakes:
Q: How often do earthquakes occur in Southern California?
A: Southern California experiences thousands of earthquakes annually, most of which are too small to be felt. However, significant earthquakes, with magnitudes greater than 4.0, occur on average several times per year.
Q: Are there any specific areas in Southern California that are more prone to earthquakes?
A: The entire Southern California region is seismically active, but certain areas along the San Andreas Fault and other major fault lines are considered higher risk zones.
Q: What should I do during an earthquake?
A: If you are indoors, drop, cover, and hold on under a sturdy piece of furniture. If you are outdoors, move away from buildings, trees, and power lines. Stay calm and follow the instructions of emergency responders.
Q: What should I do after an earthquake?
A: Check for injuries and provide first aid. Inspect your home or building for damage, and evacuate if necessary. Listen to emergency broadcasts for instructions and updates.
Tips for Earthquake Preparedness:
- Secure heavy objects that could fall during shaking.
- Identify safe spots in your home for shelter.
- Keep a first-aid kit and emergency supplies readily available.
- Practice earthquake drills with your family or workplace.
- Learn CPR and first aid.
- Stay informed about earthquake preparedness resources and updates.
Conclusion:
Southern California’s earthquake history underscores the importance of understanding the geological forces at play and developing effective preparedness strategies. While earthquakes cannot be prevented, proactive measures can significantly reduce the risks and mitigate the impacts of these natural disasters. By embracing a culture of preparedness, individuals, communities, and institutions can enhance resilience and minimize the potential for loss and disruption.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Impact of Southern California Earthquakes: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
