Understanding the MAP Sensor: A Guide to Its Function and Readings
Related Articles: Understanding the MAP Sensor: A Guide to Its Function and Readings
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the MAP Sensor: A Guide to Its Function and Readings. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the MAP Sensor: A Guide to Its Function and Readings

The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor is a crucial component in modern automotive engines, playing a vital role in determining the air density within the intake manifold. This information is essential for the engine control unit (ECU) to calculate the optimal amount of fuel to inject, ultimately impacting engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
The Role of the MAP Sensor
The MAP sensor operates on the principle of measuring the pressure within the intake manifold, which is directly related to the amount of air entering the engine. It converts this pressure reading into an electrical signal that the ECU can interpret. The sensor’s output is typically measured in kilopascals (kPa) or inches of mercury (Hg).
Factors Influencing MAP Sensor Readings
Several factors can influence the MAP sensor reading, including:
- Engine RPM: Higher RPMs generally result in higher manifold pressure.
- Throttle Position: Opening the throttle increases air intake, leading to higher manifold pressure.
- Altitude: Higher altitudes result in lower atmospheric pressure, leading to lower manifold pressure.
- Engine Load: Heavier engine loads, such as accelerating or towing, require more air, resulting in higher manifold pressure.
- Ambient Temperature: Colder temperatures lead to denser air, which translates to higher manifold pressure.
Interpreting MAP Sensor Readings
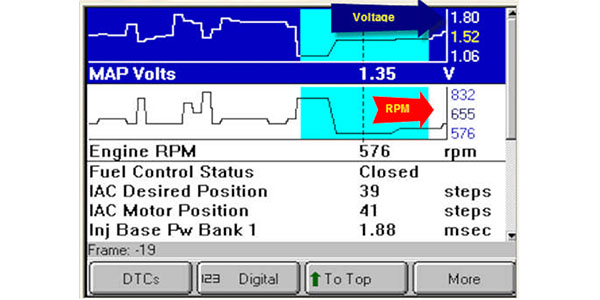
Understanding the expected MAP sensor readings for a specific engine requires consulting the manufacturer’s specifications. These specifications provide a range of acceptable readings based on engine parameters like RPM, throttle position, and load.
Typical MAP Sensor Readings
While exact readings vary significantly between engine models, here’s a general overview of expected ranges:
- Idle: At idle, the MAP sensor reading is typically low, usually in the range of 0.5 to 1.5 Hg.
- Partial Throttle: Under partial throttle, the reading increases proportionally to the throttle opening, ranging from 2 to 10 Hg.
- Full Throttle: At full throttle, the MAP sensor reading reaches its highest point, often exceeding 10 Hg, depending on the engine and load.
The Importance of Accurate MAP Sensor Readings
Accurate MAP sensor readings are essential for optimal engine performance. Here’s why:
- Fuel Efficiency: The ECU relies on the MAP sensor data to calculate the precise amount of fuel required for combustion. Inaccurate readings can lead to either too much or too little fuel, impacting fuel efficiency and emissions.
- Engine Power: An incorrect MAP sensor reading can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to power loss, misfires, and rough idling.
- Emissions Control: The ECU uses MAP sensor data to adjust ignition timing and other parameters, influencing emissions levels. Inaccurate readings can lead to higher emissions.
- Overall Performance: The MAP sensor plays a vital role in overall engine performance. Faulty or inaccurate readings can manifest in a variety of symptoms, including poor acceleration, stalling, and engine hesitation.
Troubleshooting MAP Sensor Issues
When experiencing engine problems, checking the MAP sensor is crucial. Here’s a simple troubleshooting guide:
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the MAP sensor for any visible damage, loose connections, or signs of corrosion.
- Pressure Test: Use a vacuum gauge or pressure tester to measure the actual manifold pressure and compare it to the MAP sensor reading.
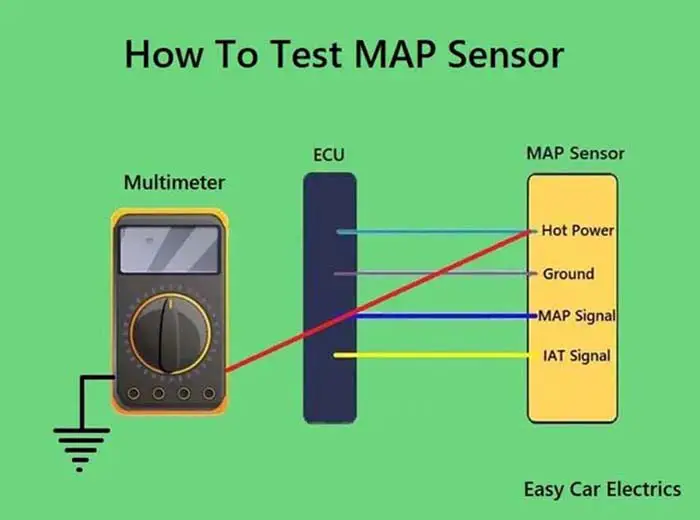
- Electrical Testing: Check the MAP sensor’s electrical connections and wiring for continuity and resistance using a multimeter.
- ECU Scan: Utilize an OBD-II scanner to read the MAP sensor data and identify any error codes related to the sensor.
FAQs
Q: What are the symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor?
A: Symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor can include:
- Poor acceleration
- Stalling
- Engine hesitation
- Rough idling
- Increased fuel consumption
- Engine misfires
- Check engine light illumination
Q: How often should I replace my MAP sensor?
A: There’s no set replacement schedule for MAP sensors. However, they can wear out over time, especially if exposed to harsh conditions. If you suspect a faulty sensor, it’s best to have it inspected by a qualified mechanic.
Q: Can I clean my MAP sensor?
A: It’s generally not recommended to clean a MAP sensor. Cleaning can damage the delicate sensor element. If you suspect contamination, it’s better to replace the sensor.
Tips for Maintaining Your MAP Sensor
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure regular engine maintenance, including air filter changes, can help prevent excessive dust and debris from reaching the MAP sensor.
- Avoid Harsh Conditions: Minimize exposure to extreme temperatures, moisture, and corrosive environments, as these can damage the sensor.
- Professional Inspection: If experiencing engine problems, have a qualified mechanic inspect the MAP sensor as part of the troubleshooting process.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor is a critical component in modern automotive engines, providing vital information to the ECU for optimal engine operation. Understanding the role of the MAP sensor, interpreting its readings, and recognizing potential issues can help ensure smooth engine performance, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the MAP Sensor: A Guide to Its Function and Readings. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
