Understanding the MAP Sensor: A Guide to Its Role and Normal Readings
Related Articles: Understanding the MAP Sensor: A Guide to Its Role and Normal Readings
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the MAP Sensor: A Guide to Its Role and Normal Readings. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the MAP Sensor: A Guide to Its Role and Normal Readings
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the MAP Sensor: A Guide to Its Role and Normal Readings
- 3.1 The MAP Sensor: A Vital Link in the Engine’s Control System
- 3.2 Understanding Normal MAP Sensor Readings
- 3.3 The Importance of a Properly Functioning MAP Sensor
- 3.4 Identifying and Addressing Issues with the MAP Sensor
- 3.5 FAQs Regarding the MAP Sensor
- 3.6 Tips for Maintaining a Healthy MAP Sensor
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the MAP Sensor: A Guide to Its Role and Normal Readings

The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor, a crucial component in modern internal combustion engines, plays a vital role in determining the amount of air entering the engine. By measuring the pressure within the intake manifold, the MAP sensor provides the engine control unit (ECU) with valuable information that influences crucial engine functions like fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions control.
The MAP Sensor: A Vital Link in the Engine’s Control System
The MAP sensor, a small, typically diaphragm-based device, is strategically positioned in the intake manifold. It measures the absolute pressure within the manifold, which reflects the amount of air being drawn into the engine. This pressure varies depending on engine load, throttle position, and atmospheric conditions.
The sensor’s output, usually in the form of a voltage signal, is transmitted to the ECU. The ECU interprets this signal, translating the pressure reading into an accurate representation of the air mass entering the engine. This information is then used to calculate the appropriate fuel-to-air ratio, optimize ignition timing, and ensure efficient combustion.
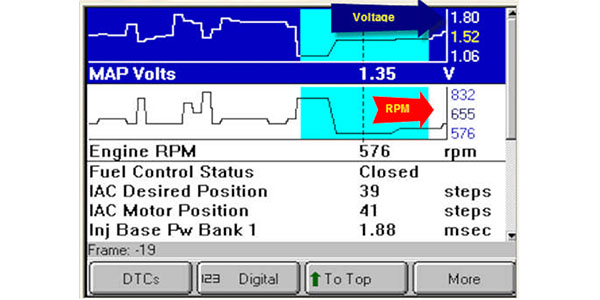
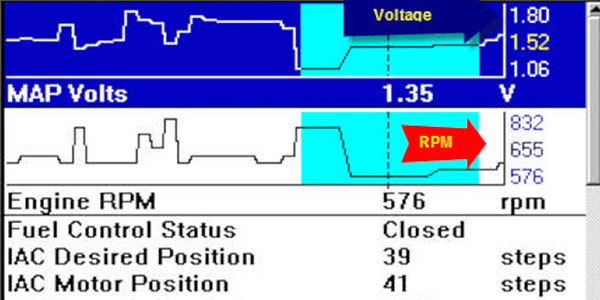
Understanding Normal MAP Sensor Readings
The normal reading of a MAP sensor varies depending on the specific engine model and operating conditions. However, there are general guidelines that can help understand the expected range:
- At Idle: The MAP sensor reading at idle is typically low, usually between 0.5 and 1.5 bar (7.3 and 21.7 psi). This reflects the minimal amount of air being drawn into the engine when it’s not under load.
- At Partial Throttle: As the throttle opens and the engine revs up, the MAP sensor reading increases proportionally. This reflects the increased airflow into the engine under partial load.
- At Full Throttle: Under full throttle, the MAP sensor reading reaches its highest value, typically around 0.8 to 1.2 bar (11.6 to 17.4 psi) depending on the engine size and design. This indicates the maximum amount of air the engine can intake.
It’s important to note that these values are merely general guidelines. Specific engine models may have different normal MAP sensor readings, and these readings can also be influenced by factors like altitude and temperature.
The Importance of a Properly Functioning MAP Sensor
A properly functioning MAP sensor is crucial for optimal engine performance and efficiency. Here’s how it impacts various engine functions:
- Fuel Injection: The ECU uses the MAP sensor reading to calculate the precise amount of fuel to inject into the engine. This ensures an optimal fuel-to-air ratio for efficient combustion and minimizes fuel consumption.
- Ignition Timing: The MAP sensor reading also helps the ECU determine the ideal ignition timing. This timing influences combustion efficiency and engine power output.
- Emissions Control: The ECU utilizes the MAP sensor reading to adjust the air-fuel mixture, minimizing harmful emissions like carbon monoxide and unburnt hydrocarbons.
- Engine Performance: A properly functioning MAP sensor ensures smooth engine operation, optimal power delivery, and improved fuel economy.
Identifying and Addressing Issues with the MAP Sensor
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to various engine problems, including:
- Rough Idle: A faulty MAP sensor can cause the engine to idle erratically or stall.
- Poor Acceleration: The engine may struggle to accelerate smoothly or experience hesitation.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: An inaccurate MAP sensor reading can lead to an overly rich fuel mixture, resulting in higher fuel consumption.
- Check Engine Light: A malfunctioning MAP sensor can trigger the check engine light, indicating a problem that needs attention.
If you suspect a faulty MAP sensor, it’s crucial to diagnose the issue properly. A mechanic can use diagnostic tools to test the sensor’s output and compare it to the expected readings. Replacing a faulty MAP sensor is generally a straightforward procedure, but it’s essential to ensure that the replacement sensor is compatible with your vehicle model.
FAQs Regarding the MAP Sensor
1. What are the common signs of a faulty MAP sensor?
Common signs include rough idle, poor acceleration, increased fuel consumption, and a check engine light.
2. Can I test the MAP sensor myself?
While a basic voltage check can be performed with a multimeter, a thorough diagnosis requires specialized tools and knowledge. It’s best to consult a mechanic for a professional diagnosis.
3. How often should I replace the MAP sensor?
MAP sensors are generally durable components, but they can wear out over time. However, regular maintenance and inspections can help identify potential issues early.
4. Can a faulty MAP sensor damage my engine?
A faulty MAP sensor can lead to improper fuel-air mixture and ignition timing, potentially causing engine damage in the long run.
5. Can I clean the MAP sensor?
While some sensors may be cleaned with a specialized cleaner, it’s generally not recommended. Cleaning can damage the sensor and may not fully resolve the issue.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy MAP Sensor
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure your vehicle undergoes regular maintenance, including air filter replacement, to prevent dust and debris from accumulating near the sensor.
- Avoid Excessive Engine Modifications: Avoid modifications that significantly alter the intake manifold pressure, as this can affect the sensor’s accuracy.
- Professional Diagnosis: If you suspect a faulty MAP sensor, consult a mechanic for professional diagnosis and repair.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor is a crucial component in modern internal combustion engines, providing the ECU with vital information about the amount of air entering the engine. This information is essential for optimal fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions control. A properly functioning MAP sensor ensures efficient engine performance, fuel economy, and reduced emissions. Understanding its role and normal readings allows drivers to identify potential problems early and take appropriate action to maintain optimal engine health.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the MAP Sensor: A Guide to Its Role and Normal Readings. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
