Understanding the Role of a 2-Bar MAP Sensor in GM Vehicles
Related Articles: Understanding the Role of a 2-Bar MAP Sensor in GM Vehicles
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Role of a 2-Bar MAP Sensor in GM Vehicles. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Role of a 2-Bar MAP Sensor in GM Vehicles
![[DIAGRAM] Gm 2 Bar Map Sensor Wiring Diagram - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://www.bmotorsports.com/shop/images/thumb-100/SNSR-03074-6.jpg.thumb_800x800_mat.jpg)
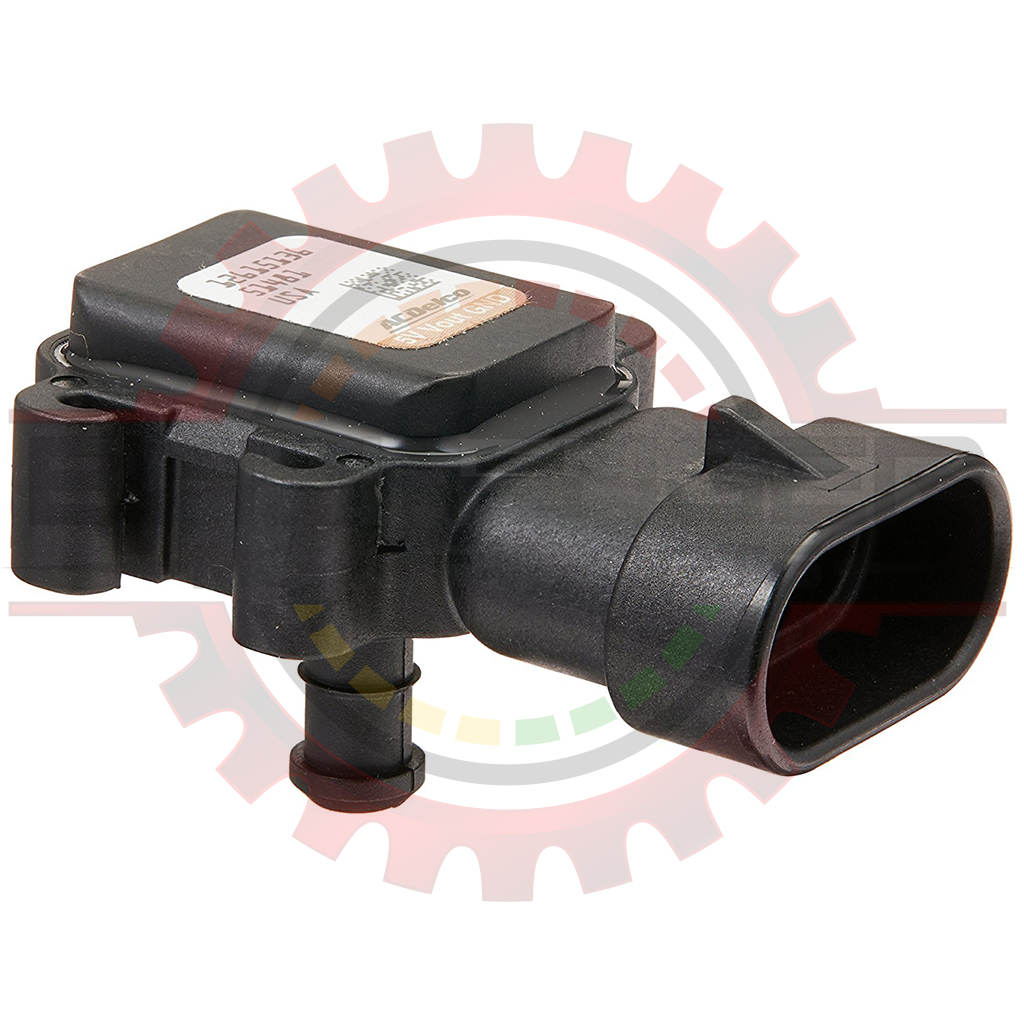
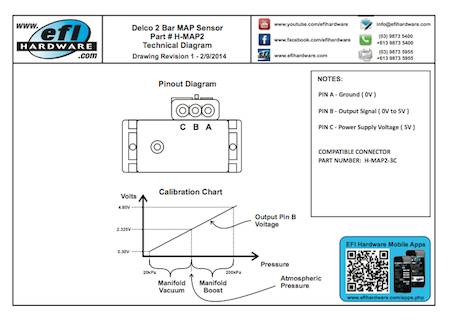
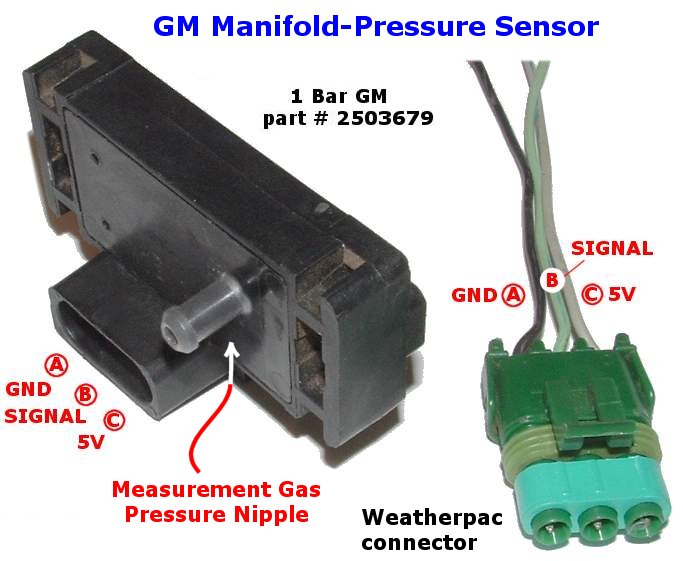
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor is a critical component in modern automotive engine management systems. Its primary function is to measure the pressure within the intake manifold, providing the engine control unit (ECU) with vital information about engine load. This data is then used to optimize fuel injection, ignition timing, and other parameters, ultimately enhancing engine performance and fuel efficiency.
The Significance of the 2-Bar MAP Sensor
The "2-bar" designation refers to the sensor’s pressure measurement range, which is typically up to 2 atmospheres (29.4 psi). This higher pressure rating distinguishes it from the more common 1-bar MAP sensors found in naturally aspirated engines.
The 2-bar MAP sensor finds its niche in vehicles equipped with forced induction systems, such as turbochargers or superchargers. These systems significantly increase the pressure within the intake manifold, exceeding the measurement capacity of a standard 1-bar sensor. By utilizing a 2-bar MAP sensor, the ECU gains accurate readings even under boosted conditions, enabling it to precisely adjust engine parameters for optimal performance and efficiency.
How the 2-Bar MAP Sensor Operates
At its core, a 2-bar MAP sensor employs a piezoresistive element, typically made of silicon. This element changes its resistance in proportion to the applied pressure. When the intake manifold pressure varies, the piezoresistive element’s resistance changes accordingly. This change in resistance is then converted into a voltage signal by the sensor’s internal circuitry. The ECU receives this voltage signal and interprets it to determine the actual manifold pressure.
Benefits of Using a 2-Bar MAP Sensor
The implementation of a 2-bar MAP sensor in boosted vehicles offers numerous advantages:
- Precise Engine Control: By accurately measuring the higher manifold pressures generated by forced induction, the 2-bar MAP sensor provides the ECU with precise data for optimal engine control. This leads to improved fuel economy, reduced emissions, and enhanced performance.
- Optimized Fuel Injection: The ECU can precisely calculate the required fuel volume based on the accurate pressure readings, ensuring efficient combustion and minimizing fuel waste.
- Precise Ignition Timing: The ECU can fine-tune ignition timing based on manifold pressure, optimizing combustion and reducing knock.
- Enhanced Performance: By ensuring optimal fuel delivery and ignition timing, the 2-bar MAP sensor contributes to increased power output and torque, maximizing the benefits of forced induction.
- Reduced Emissions: Accurate engine control enabled by the 2-bar MAP sensor minimizes fuel waste and optimizes combustion, resulting in lower emissions.
Common Problems with 2-Bar MAP Sensors
While generally reliable, 2-bar MAP sensors can experience issues over time. These problems often manifest as:
- Erratic Engine Operation: Fluctuations in the sensor’s output can lead to inconsistent fuel delivery and ignition timing, causing erratic engine operation.
- Reduced Power Output: Inaccurate pressure readings can hinder the ECU’s ability to optimize engine parameters, leading to a decrease in power output.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: Erratic fuel delivery due to a faulty sensor can result in increased fuel consumption.
- Check Engine Light: The ECU detects faulty sensor readings and triggers a check engine light, indicating the need for diagnosis and repair.
Troubleshooting and Replacing a 2-Bar MAP Sensor
Diagnosing a faulty 2-bar MAP sensor requires specialized tools and knowledge. A mechanic can use a scan tool to check for sensor codes and perform live data analysis to evaluate its performance.
If a faulty sensor is identified, replacement is typically straightforward. It involves disconnecting the sensor’s electrical connector, removing the sensor from its mounting location, and installing the new sensor in its place.
FAQs about 2-Bar MAP Sensors
Q: Can I replace a 1-bar MAP sensor with a 2-bar MAP sensor?
A: No, replacing a 1-bar MAP sensor with a 2-bar sensor is not recommended. The ECU is programmed to expect specific voltage signals from the sensor, and a 2-bar sensor will provide different readings, leading to engine malfunctions.
Q: What are the signs of a faulty 2-bar MAP sensor?
A: Common signs include erratic engine operation, reduced power output, increased fuel consumption, and a check engine light.
Q: How often should I replace the 2-bar MAP sensor?
A: There is no specific replacement interval. However, it’s recommended to replace the sensor if it exhibits signs of failure or if it’s nearing the end of its service life.
Q: Can I clean a 2-bar MAP sensor?
A: Cleaning a 2-bar MAP sensor is not recommended. The sensor’s internal components are delicate and easily damaged. If cleaning is necessary, consult a qualified mechanic.
Tips for Maintaining a 2-Bar MAP Sensor
- Regular Inspections: Inspect the sensor for any signs of damage, dirt, or debris.
- Avoid Exposing to Extreme Temperatures: Prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures can damage the sensor.
- Proper Installation: Ensure the sensor is securely installed and the electrical connector is properly connected.
- Use Quality Replacement Parts: Always use genuine or high-quality replacement parts.
Conclusion
The 2-bar MAP sensor is an essential component in modern boosted vehicles. Its ability to accurately measure high manifold pressures under forced induction conditions is crucial for optimal engine control, fuel efficiency, and performance. While generally reliable, the sensor can experience issues over time, requiring diagnosis and replacement. By understanding its role and potential problems, drivers can ensure the proper functioning of this critical component, maximizing their vehicle’s performance and longevity.

![[DIAGRAM] Gm 2 Bar Map Sensor Wiring Diagram - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://www.efihardware.com/images/2923/H-MAPDelco1BarMAPSensorWiringRevision1.jpg?cache=20150412230602)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Role of a 2-Bar MAP Sensor in GM Vehicles. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
