Understanding the Significance of a 1 Bar MAP Sensor Range in Engine Management
Related Articles: Understanding the Significance of a 1 Bar MAP Sensor Range in Engine Management
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Significance of a 1 Bar MAP Sensor Range in Engine Management. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Significance of a 1 Bar MAP Sensor Range in Engine Management

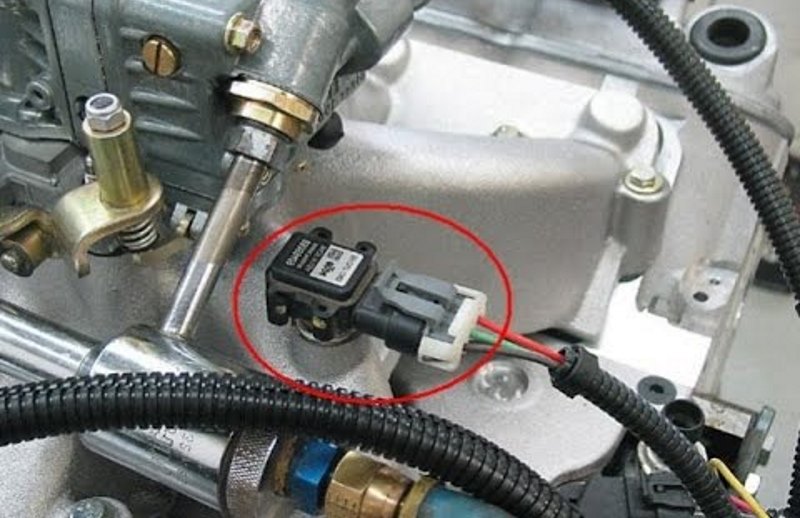
The heart of an internal combustion engine’s fuel injection system lies in its ability to precisely control the amount of air entering the cylinders. This is where the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor plays a crucial role. A MAP sensor, often referred to as a barometric pressure sensor, measures the pressure within the engine’s intake manifold. This information is then relayed to the engine control unit (ECU) which, in turn, calculates the optimal amount of fuel to inject for efficient combustion.
While MAP sensors come in various pressure ranges, a 1 bar sensor is particularly prevalent in naturally aspirated gasoline engines. This article delves into the intricacies of a 1 bar MAP sensor range, elucidating its significance in engine performance and fuel efficiency.
The Essence of Pressure Measurement
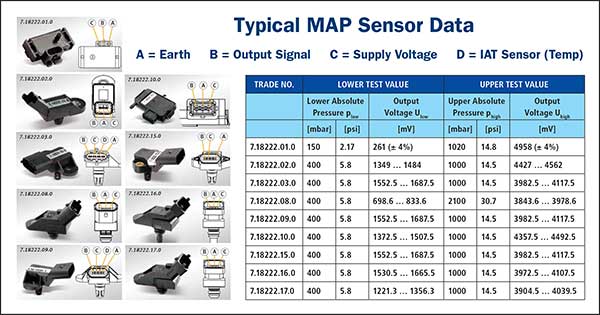
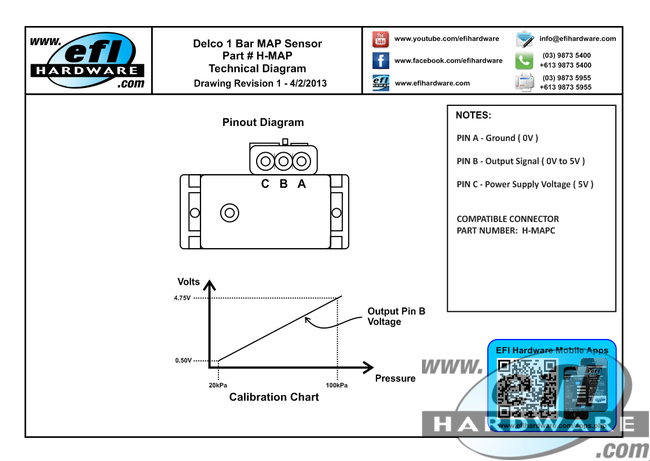
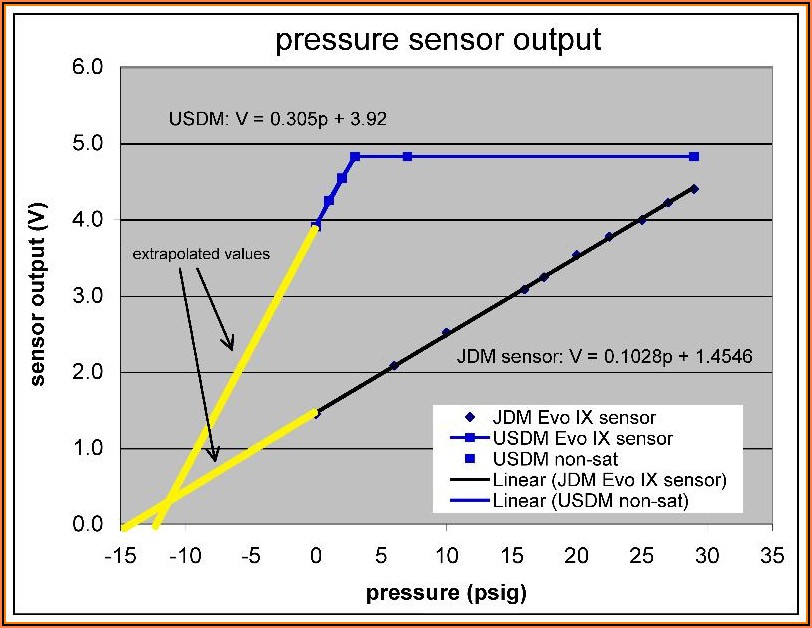
The pressure within the intake manifold directly corresponds to the amount of air present. A higher pressure indicates a larger volume of air, requiring a greater fuel injection volume to maintain the ideal air-fuel ratio. A 1 bar MAP sensor is calibrated to measure pressures ranging from 0 to 1 bar (absolute pressure), which translates to 0 to 14.5 psi (pounds per square inch) gauge pressure. This range effectively covers the typical operating pressures encountered in naturally aspirated engines.
Benefits of a 1 Bar MAP Sensor
-
Precise Fuel Delivery: The 1 bar MAP sensor’s accurate pressure readings allow the ECU to determine the precise amount of fuel needed for optimal combustion. This results in a smooth and efficient engine operation, minimizing fuel wastage and emissions.
-
Enhanced Throttle Response: The ECU, armed with real-time pressure data from the MAP sensor, can adjust the fuel injection timing and duration accordingly. This translates to a more responsive throttle, allowing the engine to react swiftly to driver input.
-
Improved Fuel Efficiency: By precisely controlling the air-fuel mixture, the 1 bar MAP sensor contributes to optimal combustion efficiency. This results in a reduction in fuel consumption, saving both money and environmental impact.
-
Reduced Emissions: The accurate air-fuel ratio maintained by the MAP sensor ensures complete combustion, minimizing harmful emissions like unburnt hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide.
Understanding the 1 Bar Range in Detail
The 1 bar range signifies the sensor’s capacity to measure pressure up to 1 atmosphere. This is a common pressure range for naturally aspirated engines, where the intake manifold pressure rarely exceeds 1 bar. However, for turbocharged engines, which generate significantly higher pressures, sensors with higher pressure ranges are required.
Calibration and Accuracy
The 1 bar MAP sensor’s accuracy is paramount for optimal engine performance. During the manufacturing process, each sensor undergoes rigorous calibration to ensure precise pressure readings within its specified range. This calibration involves a comparison against a known standard, ensuring that the sensor output accurately reflects the actual intake manifold pressure.
Factors Affecting MAP Sensor Performance
Several factors can influence the performance of a 1 bar MAP sensor:
-
Temperature Variations: Extreme temperatures can affect the sensor’s internal components, potentially leading to inaccurate readings.
-
Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the intake manifold can create an inaccurate vacuum reading, affecting the sensor’s output.
-
Sensor Contamination: Dirt, debris, or oil buildup on the sensor’s diaphragm can hinder its movement, leading to inaccurate pressure readings.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial to ensure the MAP sensor’s optimal performance.
-
Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the sensor for any signs of damage, leaks, or contamination.
-
Pressure Testing: A pressure test can confirm the sensor’s accuracy and identify any leaks in the intake manifold.
-
Replacement: If the sensor is damaged or faulty, it should be replaced with a new one of the same specification.
FAQs about 1 Bar MAP Sensor Range
Q: What happens if the MAP sensor fails?
A: A faulty MAP sensor can lead to a range of issues, including poor fuel economy, rough idling, hesitation during acceleration, and even engine misfires.
Q: Can I use a different MAP sensor range?
A: Using a MAP sensor with a different pressure range than the one specified for your engine can lead to inaccurate readings and potentially damage the engine.
Q: How often should I check the MAP sensor?
A: While regular visual inspections are recommended, a professional pressure test should be performed during routine maintenance or if any engine performance issues arise.
Tips for Maintaining a 1 Bar MAP Sensor
-
Regularly inspect the sensor for signs of damage or contamination.
-
Ensure the intake manifold is free of leaks.
-
Use high-quality fuel and air filters to minimize contamination.
-
Replace the sensor if it shows signs of malfunction.
Conclusion
The 1 bar MAP sensor plays a vital role in modern gasoline engine management systems. Its accurate pressure readings allow the ECU to precisely control fuel delivery, leading to enhanced engine performance, improved fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions. Understanding the sensor’s range, calibration, and potential issues is essential for maintaining optimal engine health and achieving maximum fuel economy. By implementing regular maintenance and troubleshooting practices, drivers can ensure their 1 bar MAP sensor continues to perform flawlessly, contributing to a smooth and efficient driving experience.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Significance of a 1 Bar MAP Sensor Range in Engine Management. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
