Understanding the Significance of a 100 kPa Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Reading
Related Articles: Understanding the Significance of a 100 kPa Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Reading
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Significance of a 100 kPa Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Reading. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Significance of a 100 kPa Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Reading

The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor, a crucial component in modern internal combustion engines, plays a vital role in determining the optimal air-fuel mixture for combustion. This sensor measures the absolute pressure within the engine’s intake manifold, providing critical information to the engine control unit (ECU). This data is then used to calculate the amount of fuel injected into the cylinders, ensuring efficient combustion and optimal engine performance.
The Essence of Manifold Absolute Pressure
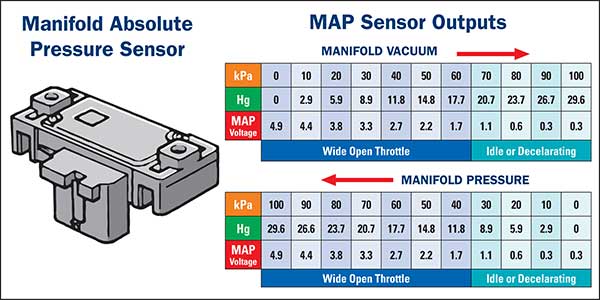
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) refers to the pressure within the engine’s intake manifold, a crucial parameter for determining the amount of air entering the cylinders. This pressure is measured in kilopascals (kPa), with a reading of 100 kPa representing a specific condition within the intake manifold.
Interpreting a 100 kPa MAP Sensor Reading
A 100 kPa MAP sensor reading signifies a specific pressure within the intake manifold, indicating a particular engine operating condition. This reading can be interpreted in relation to atmospheric pressure, which is approximately 101.3 kPa at sea level.
A 100 kPa MAP reading indicates that the pressure within the intake manifold is slightly lower than atmospheric pressure. This is a typical reading for an engine at idle or under light load, where the throttle plate is partially closed, restricting airflow.
Factors Influencing MAP Sensor Readings
Several factors influence the MAP sensor reading, including:
- Engine Speed: As engine speed increases, the vacuum within the intake manifold decreases, resulting in a higher MAP reading.
- Throttle Position: When the throttle is opened, more air enters the manifold, increasing the pressure and leading to a higher MAP reading.
- Altitude: At higher altitudes, atmospheric pressure decreases, leading to a lower MAP reading.
- Engine Load: Under heavy load, the vacuum within the intake manifold decreases, resulting in a higher MAP reading.
- Engine Temperature: Engine temperature can also slightly influence MAP readings.
The Importance of a Precise MAP Sensor Reading
A precise MAP sensor reading is essential for optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- Fuel-Air Mixture Control: The ECU utilizes the MAP sensor reading to calculate the appropriate amount of fuel to inject into the cylinders, ensuring an optimal air-fuel mixture for combustion. An inaccurate reading can lead to a lean or rich mixture, affecting engine performance and emissions.
- Engine Timing Control: The MAP sensor reading also plays a role in controlling the engine timing, ensuring efficient combustion and optimal power output.
- Emissions Control: A precise MAP sensor reading is crucial for maintaining optimal emissions levels by contributing to the accurate calculation of the air-fuel mixture.
Potential Issues Arising from a Faulty MAP Sensor
A faulty MAP sensor can lead to several issues, including:
- Poor Engine Performance: An inaccurate MAP sensor reading can result in an incorrect fuel-air mixture, leading to engine hesitation, rough idling, and reduced power output.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: A faulty MAP sensor can lead to an overly rich or lean fuel mixture, increasing fuel consumption.
- Emissions Problems: An inaccurate MAP sensor reading can cause the engine to run outside of its optimal operating range, leading to increased emissions.
- Check Engine Light: A malfunctioning MAP sensor can trigger the check engine light, indicating a need for diagnosis and repair.
Diagnosing a Faulty MAP Sensor
Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor requires a combination of visual inspection, diagnostic testing, and performance evaluation.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the MAP sensor for signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or corrosion.
- Diagnostic Testing: Utilize a scan tool to read the MAP sensor data and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Performance Evaluation: Observe the engine’s performance, noting any symptoms such as hesitation, rough idling, or reduced power output.
Replacing a Faulty MAP Sensor
Replacing a faulty MAP sensor is a relatively straightforward process that can be performed by a qualified mechanic. The replacement process involves disconnecting the sensor from the wiring harness, removing the sensor from its mounting location, and installing the new sensor.
FAQs about MAP Sensor Readings
Q: What is a typical MAP sensor reading at idle?
A: A typical MAP sensor reading at idle is around 90-100 kPa, depending on the engine and its operating conditions.
Q: What is a typical MAP sensor reading at full throttle?
A: A typical MAP sensor reading at full throttle can vary significantly depending on the engine and its operating conditions, but it can range from 100 kPa to several hundred kPa.
Q: What does a low MAP sensor reading indicate?
A: A low MAP sensor reading can indicate a vacuum leak, a blocked intake manifold, or a faulty MAP sensor.
Q: What does a high MAP sensor reading indicate?
A: A high MAP sensor reading can indicate a restricted exhaust system, a faulty MAP sensor, or an issue with the throttle position sensor.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy MAP Sensor
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect the MAP sensor for signs of damage or corrosion.
- Clean Intake Manifold: Regularly clean the intake manifold to prevent buildup of debris that can affect the MAP sensor’s operation.
- Avoid Using Low-Quality Fuel: Using low-quality fuel can lead to deposits in the intake manifold, affecting the MAP sensor’s accuracy.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor plays a critical role in ensuring optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. A precise MAP sensor reading is essential for the ECU to accurately calculate the fuel-air mixture, engine timing, and other critical parameters.
Understanding the significance of a 100 kPa MAP sensor reading and the factors influencing this reading provides valuable insight into the operation of modern internal combustion engines. By monitoring the MAP sensor reading and addressing any issues promptly, drivers can ensure optimal engine performance and longevity.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Significance of a 100 kPa Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Reading. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
