Understanding the Significance of GA MAP Testing Scores: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Significance of GA MAP Testing Scores: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Significance of GA MAP Testing Scores: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Significance of GA MAP Testing Scores: A Comprehensive Guide
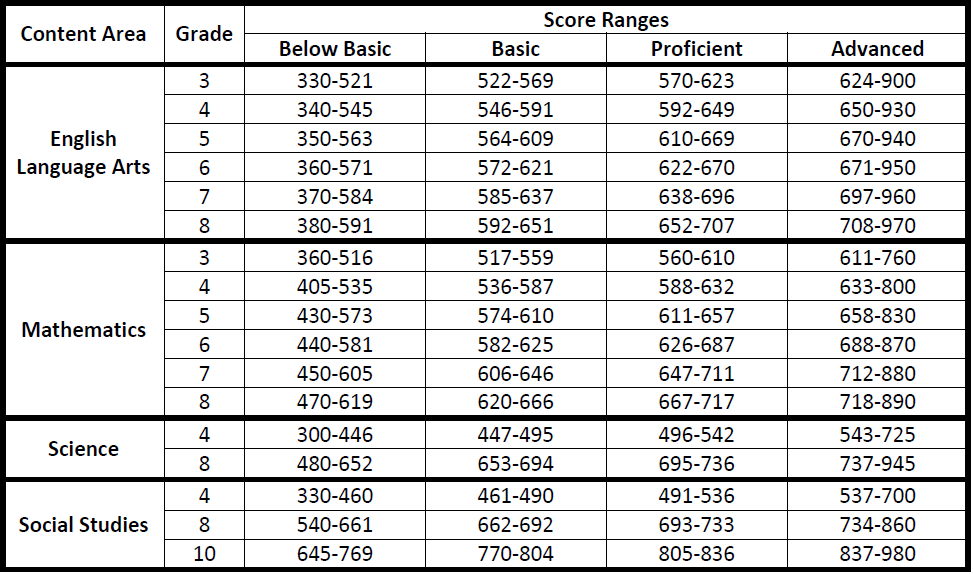
The Georgia Milestones Assessment System (GA Milestones) is a comprehensive system of standardized assessments administered to students in Georgia public schools. These assessments, including the Georgia Assessment of Mathematics Proficiency (GA MAP), play a crucial role in evaluating student performance and guiding educational decisions. This article provides a detailed exploration of GA MAP testing scores, their significance, and their implications for students, educators, and the educational system as a whole.
The GA MAP: A Foundation for Mathematics Proficiency
The GA MAP, a key component of the GA Milestones, is a standardized test designed to measure student proficiency in mathematics. It is administered annually to students in grades 3-8 and is aligned with the Georgia Standards of Excellence (GSE) for Mathematics. The GA MAP assesses a wide range of mathematical concepts and skills, including:
- Number and Operations: Understanding number systems, performing operations with numbers, and solving problems involving fractions, decimals, and percentages.
- Algebra: Solving equations and inequalities, working with functions, and understanding patterns and relationships.
- Geometry: Analyzing geometric shapes, understanding spatial reasoning, and applying geometric concepts to solve problems.
- Measurement and Data Analysis: Measuring and interpreting data, using statistical concepts, and applying measurement principles.
Understanding GA MAP Scores
GA MAP scores are reported on a scale from 100 to 800, with higher scores indicating greater proficiency in mathematics. The scores are categorized into five performance levels:
- Level 5: Exceeds Standards: Students demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the assessed content and can apply their knowledge and skills to complex problems.
- Level 4: Meets Standards: Students demonstrate a strong understanding of the assessed content and can apply their knowledge and skills to a variety of problems.
- Level 3: Approaches Standards: Students demonstrate a basic understanding of the assessed content and can apply their knowledge and skills to some problems.
- Level 2: Below Standards: Students demonstrate a limited understanding of the assessed content and need further support to develop their skills.
- Level 1: Far Below Standards: Students demonstrate a very limited understanding of the assessed content and require significant support to develop their skills.
The Importance of GA MAP Scores
GA MAP scores hold significant importance for various stakeholders in the education system:
For Students:
- Identify Strengths and Weaknesses: GA MAP scores provide students with valuable insights into their strengths and weaknesses in mathematics. This information can help them focus on areas where they need improvement and develop strategies for achieving their academic goals.
- Track Progress: GA MAP scores allow students to track their progress over time and identify areas where they have made significant gains. This can boost their confidence and motivation to continue learning.
- Measure Growth: GA MAP scores are used to measure student growth over time, providing a clear picture of their academic progress and identifying areas where they may need additional support.
For Educators:
- Inform Instruction: GA MAP scores provide valuable data that educators can use to inform their instructional practices. By analyzing student performance on specific concepts and skills, educators can tailor their teaching strategies to address the needs of individual students.
- Identify Areas for Improvement: GA MAP scores can highlight areas where students are struggling and identify specific concepts or skills that need to be revisited or reinforced.
- Monitor Student Progress: GA MAP scores allow educators to monitor student progress over time and make adjustments to their teaching strategies as needed.
For Schools and Districts:
- Measure School Effectiveness: GA MAP scores are used to evaluate school effectiveness and identify areas where improvement is needed. This information can guide the development of school-wide improvement plans and interventions.
- Compare Performance: GA MAP scores allow schools and districts to compare their performance to other schools and districts in the state. This data can be used to identify best practices and share resources.
- Accountability: GA MAP scores are used to hold schools and districts accountable for student performance and to ensure that all students have access to a quality education.
Factors Influencing GA MAP Scores
A multitude of factors can influence a student’s GA MAP score, including:
- Student Background and Preparation: A student’s prior knowledge, learning experiences, and home environment can significantly impact their performance on the GA MAP.
- Instructional Quality: The quality of instruction a student receives in mathematics can play a significant role in their understanding of the subject and their ability to perform well on the assessment.
- Access to Resources: Students who have access to quality learning materials, technology, and support services are more likely to succeed on the GA MAP.
- Test Anxiety: Test anxiety can negatively impact a student’s performance on any standardized test, including the GA MAP.
Addressing Challenges and Promoting Equity
Recognizing the potential impact of these factors, educators and policymakers are actively working to address challenges and promote equity in GA MAP testing. This includes:
- Providing Equitable Access to Resources: Ensuring that all students have access to high-quality instruction, learning materials, and support services regardless of their background or location.
- Addressing Test Anxiety: Implementing strategies to reduce test anxiety, such as providing students with test-taking strategies and fostering a positive and supportive testing environment.
- Focusing on Deeper Learning: Shifting the focus from rote memorization to deeper understanding and application of mathematical concepts.
- Utilizing Data to Inform Instruction: Using GA MAP data to inform instructional practices and tailor teaching strategies to meet the needs of individual students.
FAQs about GA MAP Testing Scores
1. What are the consequences of failing the GA MAP?
While there are no direct consequences for failing the GA MAP, a low score may indicate that a student needs additional support in mathematics. Students who score below a certain threshold may be required to participate in targeted interventions or receive additional instruction to help them improve their skills.
2. How are GA MAP scores used to determine a student’s grade?
GA MAP scores are not directly used to determine a student’s grade. However, they can be used to provide information about a student’s progress and to inform the development of individualized learning plans.
3. How often is the GA MAP administered?
The GA MAP is administered annually to students in grades 3-8.
4. What can parents do to help their children prepare for the GA MAP?
Parents can help their children prepare for the GA MAP by encouraging them to practice their math skills, providing them with opportunities to learn new concepts, and creating a supportive learning environment at home.
5. Are there any resources available to help students prepare for the GA MAP?
Yes, there are a variety of resources available to help students prepare for the GA MAP, including practice tests, online tutorials, and study guides.
Tips for Improving GA MAP Scores
- Encourage Practice: Encourage students to regularly practice their math skills through problem-solving activities, games, and online resources.
- Foster a Growth Mindset: Emphasize that learning is a process and that mistakes are opportunities for growth.
- Provide Targeted Support: Identify areas where students are struggling and provide them with additional support and instruction.
- Use Technology Effectively: Utilize technology tools to enhance learning and provide personalized instruction.
- Create a Positive Learning Environment: Foster a positive and supportive learning environment that encourages students to ask questions, take risks, and embrace challenges.
Conclusion
GA MAP testing scores play a pivotal role in evaluating student performance and guiding educational decisions in Georgia. They provide valuable insights into student proficiency in mathematics, informing instructional practices, and helping educators identify areas for improvement. While the scores themselves are not the sole determinant of student success, they serve as a valuable tool for measuring progress, identifying gaps in understanding, and guiding interventions. By understanding the significance of GA MAP scores and implementing strategies to address challenges and promote equity, educators can ensure that all students have the opportunity to achieve their full potential in mathematics.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Significance of GA MAP Testing Scores: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
