Understanding the Symptoms of a Faulty Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP)
Related Articles: Understanding the Symptoms of a Faulty Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP)
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Symptoms of a Faulty Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP). Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Symptoms of a Faulty Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP)

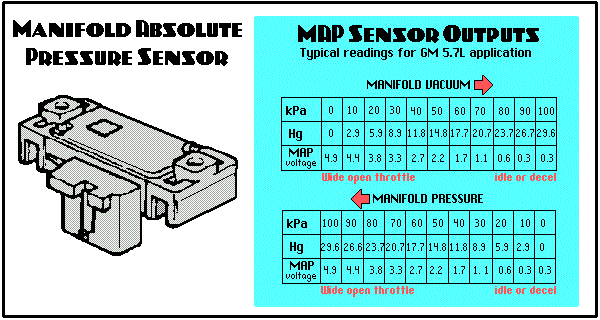
The manifold absolute pressure sensor (MAP) plays a crucial role in a vehicle’s engine management system. It measures the pressure within the intake manifold, providing the engine control unit (ECU) with vital information about engine load. This data is then used to regulate fuel injection, ignition timing, and other critical parameters, ensuring optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
However, when the MAP sensor malfunctions, it can lead to a range of issues, affecting the vehicle’s drivability and potentially causing damage to the engine. Identifying these symptoms early is essential for prompt diagnosis and repair, preventing further complications.
Common Symptoms of a Faulty MAP Sensor:
1. Engine Stalling or Rough Idle: A faulty MAP sensor can provide inaccurate pressure readings to the ECU, leading to incorrect fuel and ignition timing adjustments. This can result in the engine stalling, particularly at idle, or experiencing rough idling, characterized by erratic engine vibrations and inconsistent RPM readings.
2. Poor Acceleration and Reduced Power: A malfunctioning MAP sensor can hinder the engine’s ability to deliver optimal power. The ECU, relying on inaccurate pressure data, may not provide the appropriate fuel and ignition adjustments for efficient combustion, leading to sluggish acceleration and reduced overall power output.
3. Engine Misfire: The inaccurate pressure readings from a faulty MAP sensor can disrupt the timing of the spark plugs, causing misfires. This is characterized by a jerking or sputtering sensation during acceleration, accompanied by a rough engine sound.
4. Increased Fuel Consumption: A faulty MAP sensor can result in the ECU injecting more fuel than necessary, leading to increased fuel consumption. This is because the inaccurate pressure readings can cause the ECU to overcompensate, resulting in a richer fuel mixture that burns less efficiently.
5. Check Engine Light (CEL) Illumination: The ECU constantly monitors the MAP sensor’s readings and will trigger the CEL if it detects inconsistencies or malfunctions. The CEL may be accompanied by a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that provides further information about the specific issue with the MAP sensor.
6. Difficulty Starting the Engine: In severe cases, a faulty MAP sensor can make it difficult to start the engine. The inaccurate pressure readings can lead to incorrect fuel and ignition adjustments, making it challenging for the engine to ignite properly.
7. Erratic Idle Speed: A faulty MAP sensor can lead to fluctuations in the engine’s idle speed. The ECU, relying on inaccurate pressure data, may adjust the idle speed incorrectly, resulting in inconsistent RPM readings and a fluctuating idle.
8. Black Smoke from Exhaust: A faulty MAP sensor can lead to excessive fuel being injected into the engine, resulting in incomplete combustion. This can produce black smoke from the exhaust, indicating a rich fuel mixture.
9. Engine Backfire: In some cases, a faulty MAP sensor can lead to backfires, particularly during acceleration. This occurs when the fuel-air mixture ignites prematurely in the exhaust manifold, producing a loud popping sound.
Importance of a Functional MAP Sensor:
The MAP sensor is a critical component in modern engine management systems. Its accurate readings are essential for:
- Optimizing Fuel Efficiency: By providing accurate pressure data, the MAP sensor enables the ECU to adjust fuel injection precisely, ensuring optimal fuel consumption and reducing emissions.
- Maintaining Engine Performance: The MAP sensor plays a vital role in ensuring smooth engine operation by providing the ECU with accurate information about engine load and allowing for appropriate adjustments to fuel and ignition timing.
- Protecting the Engine: A faulty MAP sensor can lead to engine damage by causing misfires, incomplete combustion, and excessive fuel injection.
FAQs Regarding Faulty MAP Sensors:
Q: What are the potential causes of a faulty MAP sensor?
A: Several factors can contribute to a faulty MAP sensor, including:
- Wear and Tear: Over time, the sensor’s internal components can wear out, leading to inaccurate readings.
- Exposure to Extreme Temperatures: Exposure to extreme heat or cold can damage the sensor’s internal components.
- Contamination: Dust, dirt, or other contaminants can clog the sensor’s intake, affecting its ability to measure pressure accurately.
- Electrical Malfunctions: Faulty wiring or connectors can disrupt the sensor’s communication with the ECU.
Q: Can a faulty MAP sensor be repaired?
A: MAP sensors are generally not repairable. If the sensor is malfunctioning, it typically needs to be replaced.
Q: How much does it cost to replace a MAP sensor?
A: The cost of replacing a MAP sensor varies depending on the vehicle’s make and model. However, it is generally a relatively inexpensive repair, with parts costing around $20 to $100 and labor costs varying depending on the mechanic.
Q: Can I drive my car with a faulty MAP sensor?
A: While it is possible to drive with a faulty MAP sensor, it is not recommended. The inaccurate pressure readings can lead to poor fuel economy, reduced engine performance, and potential damage to the engine.
Tips for Maintaining a MAP Sensor:
- Regularly Inspect the Sensor: Inspect the MAP sensor for any signs of damage, contamination, or loose connections.
- Clean the Sensor: If the sensor is dirty, clean it with a mild solvent and a soft brush.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Protect the sensor from exposure to extreme heat or cold.
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Using high-quality fuel can help prevent contamination of the sensor.
Conclusion:
A functioning MAP sensor is crucial for ensuring optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity. Recognizing the symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor and addressing the issue promptly can prevent further complications and protect your vehicle’s engine from potential damage.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Symptoms of a Faulty Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP). We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
