Unlocking Network Security: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap Scanning
Related Articles: Unlocking Network Security: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap Scanning
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Network Security: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap Scanning. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking Network Security: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap Scanning
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking Network Security: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap Scanning
- 3.1 Understanding Nmap: A Network Security Swiss Army Knife
- 3.2 Nmap’s Role in Network Security Assessments
- 3.3 Beyond the Basics: Advanced Nmap Techniques
- 3.4 Ethical Considerations and Legal Implications
- 3.5 FAQs about Nmap Scanning
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Nmap Scanning
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unlocking Network Security: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap Scanning

In the digital landscape, where information flows freely and systems are interconnected, safeguarding networks from vulnerabilities and malicious actors is paramount. Network security assessments are crucial for identifying potential weaknesses and implementing robust defense mechanisms. A cornerstone of these assessments is the use of network scanning tools, with Nmap (Network Mapper) standing out as a powerful and versatile tool for network exploration and security analysis. This article delves into the intricacies of Nmap scanning, exploring its capabilities, applications, and significance in modern network security practices.
Understanding Nmap: A Network Security Swiss Army Knife
Nmap is an open-source network scanner designed to discover hosts and services on a computer network. Its versatility lies in its ability to perform a wide range of scans, from simple port scans to complex vulnerability assessments. Nmap’s core functionalities include:
- Host Discovery: Identifying active hosts on a network by sending network packets and analyzing responses.
- Port Scanning: Detecting open ports on target hosts, revealing potential services running on those ports.
- Operating System Detection: Identifying the operating system running on target hosts based on network response patterns.
- Service Version Detection: Determining the versions of services running on open ports, enabling identification of potential vulnerabilities.
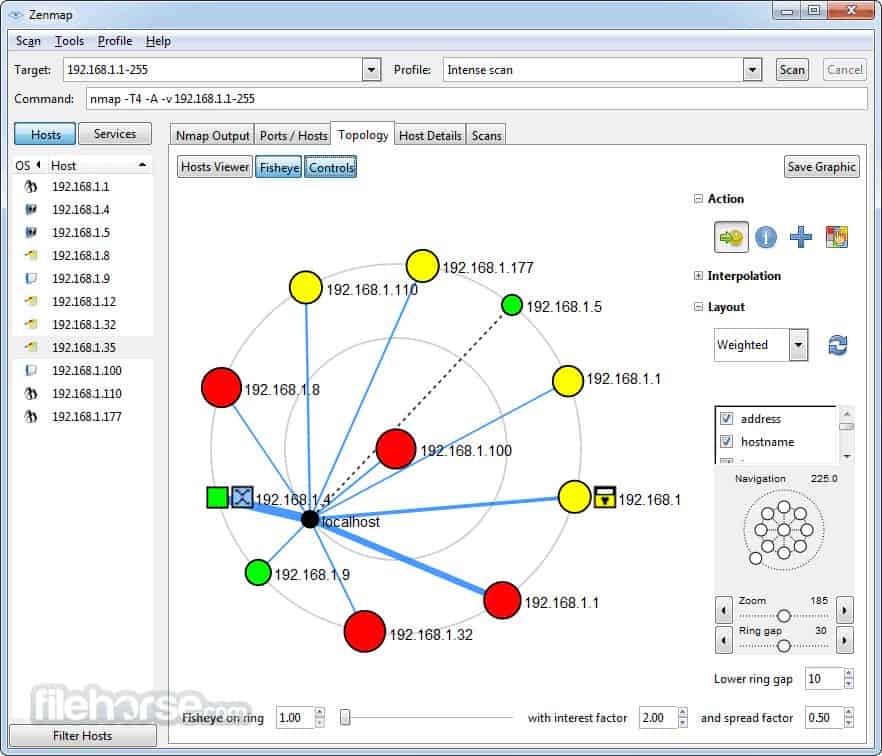
- Network Mapping: Creating a visual representation of the network topology, including devices, connections, and services.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Identifying known vulnerabilities in target systems, based on discovered services and operating systems.
Nmap’s flexibility stems from its diverse scanning techniques, ranging from simple TCP/UDP port scans to more advanced techniques like stealth scans, SYN scans, and Xmas scans. Each technique offers different advantages and disadvantages, allowing users to tailor their scans based on specific requirements and network security objectives.
Nmap’s Role in Network Security Assessments
Nmap plays a crucial role in various network security assessments, including:
- Network Discovery and Inventory: Nmap allows network administrators to map their network infrastructure, identifying all devices and services present. This information is essential for maintaining an accurate inventory of network assets and managing security policies.
- Vulnerability Identification: Nmap’s vulnerability scanning capabilities enable security professionals to identify known vulnerabilities in network devices and applications. This information empowers them to prioritize remediation efforts and mitigate potential risks.
- Security Posture Assessment: By performing comprehensive scans, Nmap provides valuable insights into the overall security posture of a network. This includes identifying potential weaknesses, misconfigurations, and exposed services.
- Penetration Testing: Nmap is a valuable tool for penetration testers, who use it to simulate real-world attacks and identify exploitable vulnerabilities. This information allows them to assess the effectiveness of security controls and recommend improvements.
- Incident Response: During security incidents, Nmap can be used to gather information about compromised systems, identify attackers, and trace the spread of malware. This information is crucial for containing the incident and restoring network security.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Nmap Techniques
Nmap’s capabilities extend beyond basic scanning functionalities. Advanced techniques include:
- Script Scanning: Nmap offers a comprehensive library of scripts that automate vulnerability checks, service detection, and other security assessments. These scripts can be used to identify specific vulnerabilities, perform targeted scans, and gather detailed information about network devices.
- NSE (Nmap Scripting Engine): Nmap’s NSE allows users to write custom scripts for specific tasks, enhancing its versatility and enabling tailored security assessments.
- NmapGUI: Nmap’s graphical user interface (GUI) provides a user-friendly interface for executing scans and visualizing scan results. This simplifies the process of using Nmap for both beginners and experienced users.
Ethical Considerations and Legal Implications
While Nmap is a powerful tool for security professionals, it is crucial to understand its ethical implications and legal ramifications. Unauthorized scanning of networks can be considered illegal in many jurisdictions and can result in legal consequences. It is essential to obtain proper authorization before scanning any network, ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
FAQs about Nmap Scanning
1. Is Nmap legal to use?
Nmap itself is a legal tool. However, its use must be ethical and within the bounds of applicable laws and regulations. Unauthorized scanning of networks can be illegal, and it is essential to obtain proper authorization before performing any scans.
2. What are the risks associated with using Nmap?
While Nmap is a valuable tool for security professionals, it can also be misused by malicious actors. Risks associated with using Nmap include:
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Nmap’s ability to send large volumes of network traffic can be exploited to launch DoS attacks, overwhelming target systems and disrupting their availability.
- Unauthorized Access: Nmap can be used to identify vulnerable systems and gain unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Misuse for Malicious Purposes: Nmap’s capabilities can be misused by malicious actors to conduct reconnaissance, identify targets, and launch attacks.
3. How can I protect my network from Nmap scans?
Several strategies can be employed to mitigate the risks associated with Nmap scans:
- Firewall Configuration: Implementing a robust firewall configuration can block incoming Nmap scans and prevent unauthorized access to network resources.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDS can monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns, including Nmap scans, and alert administrators to potential threats.
- Network Segmentation: Dividing the network into smaller segments can limit the scope of Nmap scans and prevent attackers from gaining access to sensitive information.
- Port Hardening: Disabling unnecessary ports and services can reduce the attack surface and minimize the potential impact of Nmap scans.
4. What are some best practices for using Nmap?
- Obtain Proper Authorization: Always obtain permission before scanning any network, ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
- Use Nmap Responsibly: Avoid scanning networks without authorization, as this can be illegal and unethical.
- Minimize the Impact of Scans: Use Nmap’s stealth scan options to minimize the impact on network performance and avoid triggering security alerts.
- Stay Updated: Keep Nmap and its scripts updated to ensure compatibility with the latest network devices and security protocols.
Tips for Effective Nmap Scanning
- Start with Basic Scans: Begin with simple port scans to identify active hosts and open ports.
- Use Script Scanning: Leverage Nmap’s extensive script library to automate vulnerability checks and gather detailed information about network devices.
- Combine Techniques: Combine different Nmap techniques to achieve comprehensive network security assessments.
- Analyze Scan Results: Carefully analyze scan results to identify potential vulnerabilities and prioritize remediation efforts.
- Document Your Findings: Document all scan results, including the date, time, and purpose of the scan.
Conclusion
Nmap is an indispensable tool for network security professionals, offering a wide range of functionalities for network exploration, vulnerability assessment, and penetration testing. Its versatility, combined with its open-source nature and active community support, makes it a powerful asset for safeguarding networks from malicious actors. Understanding Nmap’s capabilities, ethical considerations, and legal implications is crucial for utilizing this tool effectively and responsibly. By implementing best practices and employing advanced techniques, security professionals can leverage Nmap to enhance network security, mitigate risks, and ensure the integrity of critical data and systems.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Network Security: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap Scanning. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
