Unraveling the 2003 Honda CR-V’s MAP Sensor: Location, Function, and Importance
Related Articles: Unraveling the 2003 Honda CR-V’s MAP Sensor: Location, Function, and Importance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the 2003 Honda CR-V’s MAP Sensor: Location, Function, and Importance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the 2003 Honda CR-V’s MAP Sensor: Location, Function, and Importance

The 2003 Honda CR-V, a reliable and popular compact SUV, relies on a network of sensors to ensure optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. Among these crucial components is the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor, a small but vital piece of technology that plays a key role in determining the engine’s air intake and ultimately, its fuel delivery. Understanding the MAP sensor’s location, function, and importance can empower CR-V owners to better understand their vehicle’s intricate workings and troubleshoot potential issues effectively.
A Deep Dive into the MAP Sensor’s Role
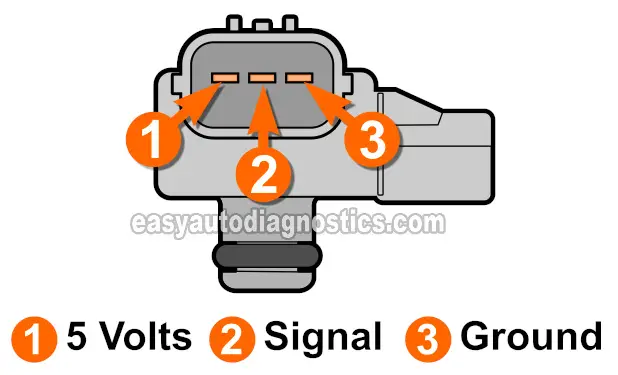
The MAP sensor is a pressure transducer, meaning it converts pressure changes into electrical signals. In the context of the 2003 CR-V’s engine, it measures the absolute pressure within the intake manifold, the chamber that connects the engine’s cylinders to the throttle body. This pressure reflects the amount of air entering the engine during each intake stroke.
The MAP sensor’s readings are crucial for the engine control unit (ECU), the "brain" of the vehicle’s engine management system. The ECU utilizes this information to calculate the appropriate amount of fuel to inject into the cylinders, ensuring a balanced air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion.
Locating the MAP Sensor: A Step-by-Step Guide
Finding the MAP sensor on a 2003 Honda CR-V requires a bit of exploration, but the process is straightforward:
- Open the Hood: Begin by safely opening the CR-V’s hood and securing it with the prop rod.
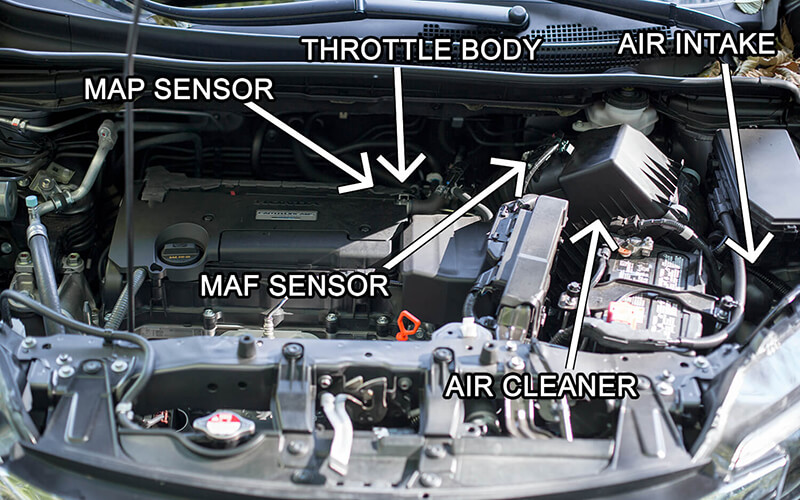
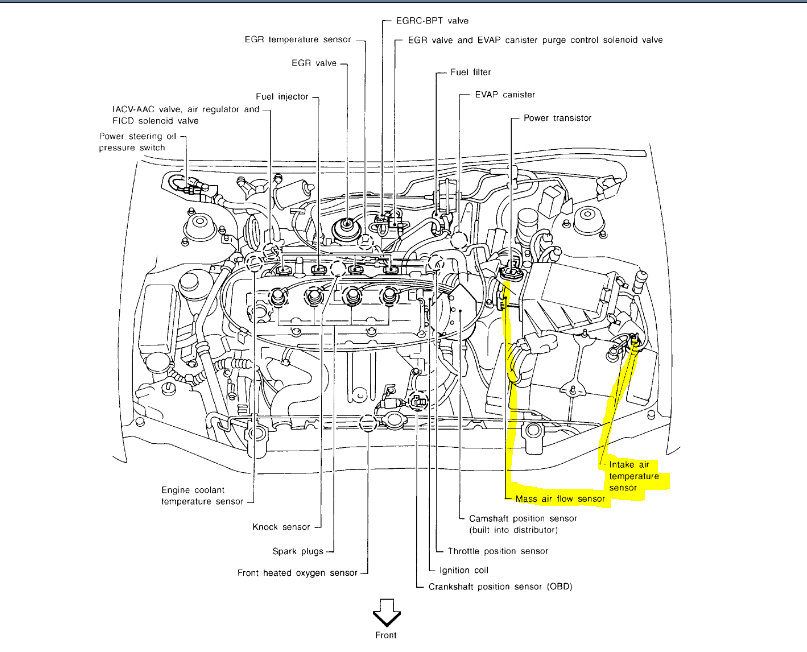
- Locate the Intake Manifold: Look for the large metal chamber with multiple hoses and connections running to it. This is the intake manifold.
- Identify the MAP Sensor: On the intake manifold, you’ll find a small, cylindrical sensor with a single electrical connector. This is the MAP sensor. It’s typically located on the side or top of the manifold, close to the throttle body.
Importance of the MAP Sensor: A Critical Engine Component
The MAP sensor’s role in the engine management system is paramount. It directly impacts:
- Fuel Efficiency: Accurate MAP sensor readings ensure the ECU delivers the precise amount of fuel required for optimal combustion, minimizing fuel waste and maximizing fuel efficiency.
- Engine Performance: A faulty MAP sensor can lead to a lean or rich air-fuel mixture, resulting in poor acceleration, engine hesitation, rough idling, and even misfires.
- Emissions Control: By contributing to the proper air-fuel mixture, the MAP sensor helps reduce harmful emissions, ensuring the vehicle complies with environmental regulations.
Understanding Common MAP Sensor Issues
While MAP sensors are designed for durability, they can encounter issues over time:
- Contamination: Dust, dirt, or oil buildup can affect the sensor’s readings, leading to inaccurate data and engine problems.
- Electrical Malfunction: A damaged electrical connector or wiring can disrupt the signal transmission from the MAP sensor to the ECU, causing engine issues.
- Sensor Failure: Like any electronic component, the MAP sensor can eventually fail, requiring replacement.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance Tips
Addressing potential MAP sensor issues involves a combination of observation, testing, and preventative maintenance:
- Check Engine Light: A flashing or illuminated "Check Engine" light often indicates a problem with the MAP sensor or the engine management system.
- Diagnostic Scan: A mechanic can use a diagnostic scanner to retrieve error codes from the ECU, providing insights into potential issues with the MAP sensor.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the MAP sensor for signs of contamination, damage, or loose connections.
- Pressure Testing: A mechanic can test the MAP sensor’s pressure readings to verify its functionality.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular engine maintenance, including air filter replacement and engine cleaning, can help prevent contamination and extend the life of the MAP sensor.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How often should the MAP sensor be replaced?
A: MAP sensors are typically designed to last the lifetime of the vehicle. However, if the sensor is contaminated or shows signs of failure, replacement is recommended.
Q: Can I replace the MAP sensor myself?
A: Replacing the MAP sensor is a relatively straightforward task for those with basic mechanical skills. However, if you are unfamiliar with automotive repairs, it’s advisable to consult a qualified mechanic.
Q: What are the symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor?
A: Symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor can include poor acceleration, engine hesitation, rough idling, misfires, increased fuel consumption, and a "Check Engine" light.
Q: Can a faulty MAP sensor cause the car to not start?
A: While a faulty MAP sensor is unlikely to completely prevent the engine from starting, it can contribute to difficulty starting, particularly in cold weather.
Conclusion: The MAP Sensor’s Vital Role
The MAP sensor, though seemingly small and inconspicuous, plays a crucial role in the 2003 Honda CR-V’s engine performance and fuel efficiency. Understanding its location, function, and potential issues can empower CR-V owners to better understand their vehicle’s inner workings, troubleshoot problems effectively, and ensure their vehicle operates at its peak performance. By staying informed and proactive, owners can maintain their CR-V’s reliability and longevity, enjoying the vehicle’s renowned comfort and practicality for years to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the 2003 Honda CR-V’s MAP Sensor: Location, Function, and Importance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
