Unveiling the World Through Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration of Map Sensor Images
Related Articles: Unveiling the World Through Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration of Map Sensor Images
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World Through Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration of Map Sensor Images. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World Through Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration of Map Sensor Images
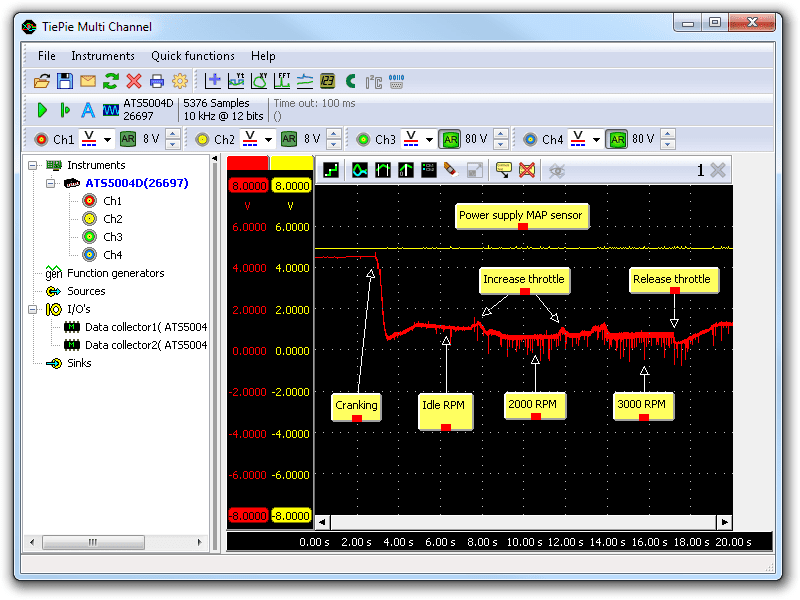
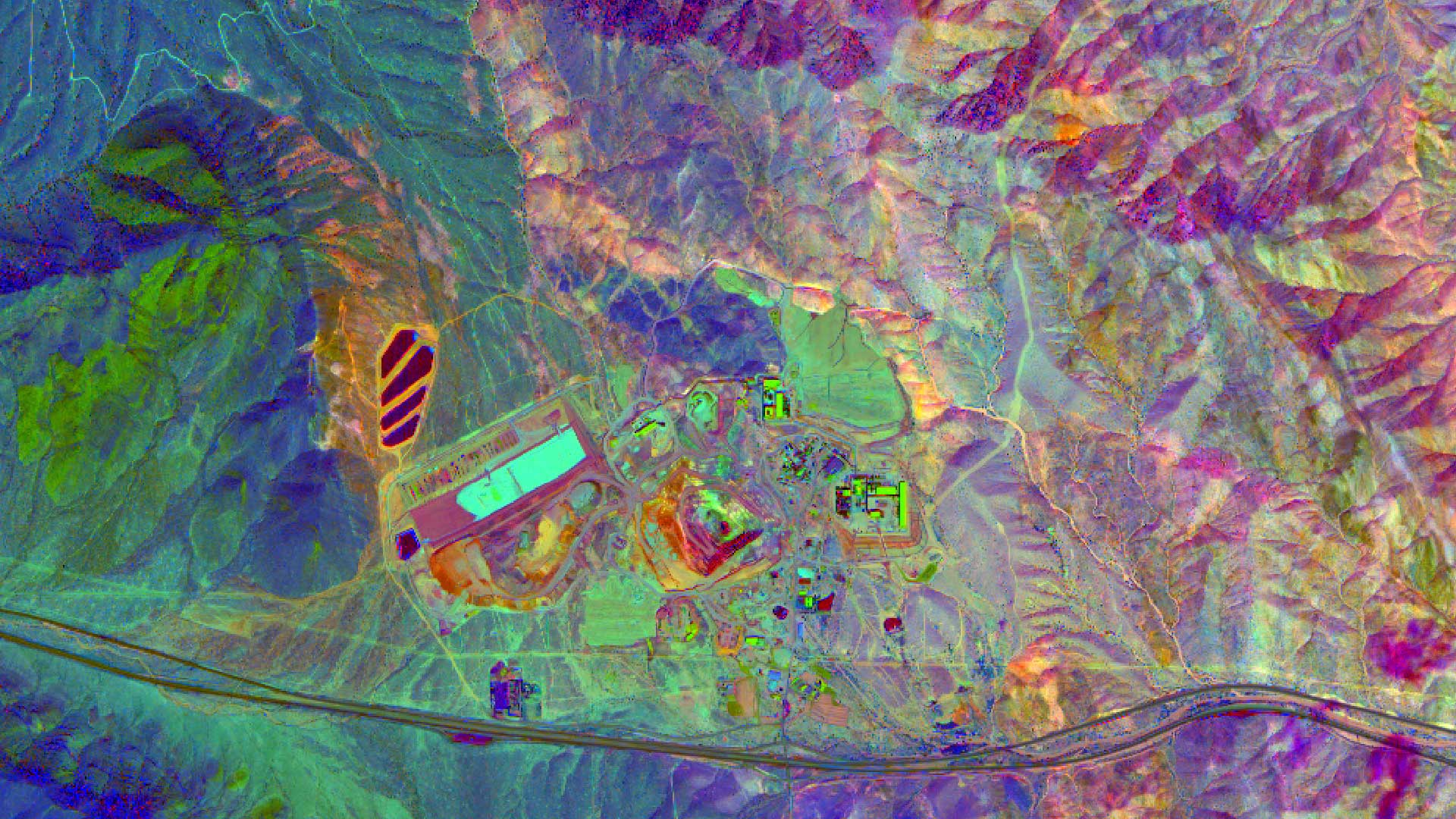
In the realm of data visualization and spatial analysis, map sensor images stand as a powerful tool, offering a unique window into the complexities of our world. These images, derived from various sensor technologies, provide valuable insights into the physical environment, human activities, and the interactions between them. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of map sensor images, exploring their origins, applications, and the significant role they play in shaping our understanding of the planet.
Understanding the Essence of Map Sensor Images
At its core, a map sensor image is a visual representation of data collected by sensors. These sensors, often mounted on satellites, aircraft, or even ground-based platforms, capture information about the Earth’s surface and atmosphere. This data, ranging from electromagnetic radiation to reflected light, is then processed and transformed into images that reveal patterns, trends, and anomalies.
The Diverse Spectrum of Sensor Technologies
The types of sensors employed in generating map sensor images are diverse, each offering unique perspectives and capabilities. Here are some prominent examples:
- Optical Sensors: These sensors capture visible light and near-infrared radiation, providing detailed imagery of land cover, vegetation, and urban environments. Examples include Landsat satellites and aerial photography.
- Radar Sensors: Utilizing radio waves, radar sensors can penetrate cloud cover and foliage, revealing terrain features, surface roughness, and even subsurface structures. Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is a powerful example, frequently used for mapping deforestation, geological formations, and disaster monitoring.
- Thermal Sensors: Sensitive to infrared radiation, thermal sensors detect heat emissions from the Earth’s surface. This allows for mapping temperature variations, identifying heat sources, and monitoring volcanic activity.
- Hyperspectral Sensors: These sensors capture a wide range of spectral bands, providing highly detailed information about the chemical composition of materials. Applications include mineral exploration, agricultural monitoring, and environmental assessment.
The Transformative Applications of Map Sensor Images
The versatility of map sensor images extends across numerous fields, enabling advancements in various domains:
- Environmental Monitoring and Management: Map sensor images play a crucial role in monitoring environmental changes, such as deforestation, land degradation, and pollution. They assist in tracking the spread of wildfires, assessing the impact of climate change, and guiding sustainable land management practices.
- Disaster Response and Risk Assessment: In the aftermath of natural disasters, map sensor images provide vital information for search and rescue operations, damage assessment, and post-disaster recovery planning. They also aid in predicting and mitigating risks associated with floods, earthquakes, and landslides.
- Urban Planning and Development: Map sensor images facilitate efficient urban planning by providing insights into population density, infrastructure development, and environmental conditions. They aid in identifying areas for urban expansion, optimizing transportation networks, and managing urban sprawl.
- Agriculture and Food Security: Map sensor images are instrumental in precision agriculture, allowing farmers to monitor crop health, identify disease outbreaks, and optimize irrigation and fertilization practices. This leads to improved crop yields and enhanced food security.
- Resource Management and Exploration: Map sensor images assist in locating and assessing natural resources, including minerals, oil and gas reserves, and water resources. They contribute to sustainable resource management and exploration efforts.
Beyond the Visual: Analyzing and Interpreting Map Sensor Images
While visually striking, map sensor images require analysis and interpretation to extract meaningful information. This involves:
- Image Processing: Enhancing the quality of images through techniques like noise reduction, geometric correction, and atmospheric correction.
- Data Extraction: Utilizing specialized software to identify and quantify features of interest, such as land cover types, building footprints, or water bodies.
- Spatial Analysis: Applying statistical and geospatial methods to analyze the spatial distribution of features and identify patterns and trends.
- Modeling and Prediction: Using map sensor images as input for predictive models, forecasting future scenarios, and informing decision-making.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Map Sensor Images
1. How are map sensor images created?
Map sensor images are created through a process involving sensors, data acquisition, processing, and visualization. Sensors capture data about the Earth’s surface, which is then converted into digital format and processed to enhance its quality and extract meaningful information. The final output is a visual representation of the data, often in the form of a map or image.
2. What are the limitations of map sensor images?
While powerful tools, map sensor images have limitations. These include:
- Cloud Cover: Optical sensors struggle to penetrate cloud cover, limiting data acquisition during cloudy periods.
- Atmospheric Effects: Atmospheric conditions can distort the captured signal, requiring correction techniques.
- Spatial Resolution: The level of detail captured by a sensor varies depending on its capabilities. Low-resolution images may not be suitable for detailed analysis.
- Temporal Resolution: The frequency of data acquisition influences the ability to monitor dynamic changes.
3. How can I access and use map sensor images?
Numerous organizations, including government agencies (e.g., NASA, USGS) and commercial providers, offer access to map sensor images. These images can be downloaded or accessed online through platforms like Google Earth Engine, ArcGIS Online, and various open-source libraries.
4. What are the ethical considerations surrounding the use of map sensor images?
The use of map sensor images raises ethical concerns related to privacy, security, and the potential for misuse. It is crucial to use these images responsibly, ensuring data security and respecting individual privacy.
Tips for Effective Utilization of Map Sensor Images
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly articulate the specific goals and questions that map sensor images are intended to address.
- Select Appropriate Data: Choose the most suitable sensor technology and data resolution based on the objectives and spatial scale of the study.
- Understand Data Limitations: Be aware of the limitations of map sensor images and consider their potential impact on the analysis and interpretation.
- Utilize Specialized Tools: Employ appropriate software and techniques for image processing, data extraction, and spatial analysis.
- Collaborate with Experts: Engage with experts in remote sensing, GIS, and related fields to ensure accurate analysis and interpretation.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Map Sensor Images
Map sensor images have emerged as a cornerstone of modern data analysis, providing unparalleled insights into the physical environment, human activities, and the intricate interplay between them. Their applications span across diverse domains, from environmental monitoring and disaster response to urban planning and resource management. As technology continues to advance, map sensor images are poised to play an even more pivotal role in addressing global challenges and shaping a sustainable future. Their ability to reveal hidden patterns, monitor critical changes, and guide informed decision-making makes them an indispensable tool for understanding and managing our planet.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World Through Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration of Map Sensor Images. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
